Page 505 - Advanced thermodynamics for engineers
P. 505
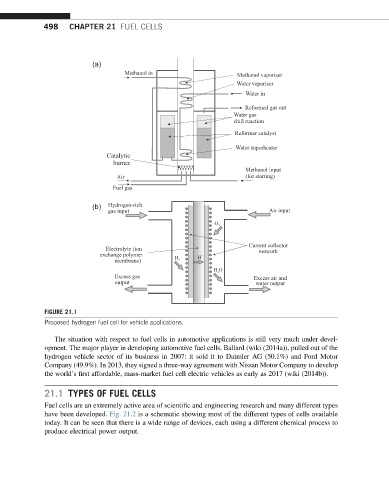
498 CHAPTER 21 FUEL CELLS
(a)
Methanol in Methanol vaporiser
Water vaporiser
Water in
Reformed gas out
Water gas
shift reaction
Reformer catalyst
Water superheater
Catalytic
burner
Methanol input
Air (for starting)
Fuel gas
(b) Hydrogen-rich
gas input Air input
O
Current collector
Electrolyte (ion
exchange polymer H H network
membrane)
HO
Excess gas Excess air and
output water output
FIGURE 21.1
Proposed hydrogen fuel cell for vehicle applications.
The situation with respect to fuel cells in automotive applications is still very much under devel-
opment. The major player in developing automotive fuel cells, Ballard (wiki (2014a)), pulled out of the
hydrogen vehicle sector of its business in 2007: it sold it to Daimler AG (50.1%) and Ford Motor
Company (49.9%). In 2013, they signed a three-way agreement with Nissan Motor Company to develop
the world’s first affordable, mass-market fuel cell electric vehicles as early as 2017 (wiki (2014b)).
21.1 TYPES OF FUEL CELLS
Fuel cells are an extremely active area of scientific and engineering research and many different types
have been developed. Fig. 21.2 is a schematic showing most of the different types of cells available
today. It can be seen that there is a wide range of devices, each using a different chemical process to
produce electrical power output.