Page 140 - Advanced Mine Ventilation
P. 140
Characteristics of Respirable Coal Dust Particles 121
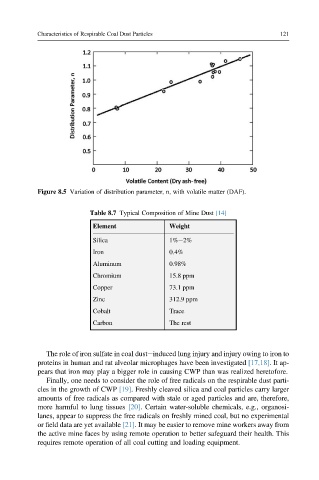
Figure 8.5 Variation of distribution parameter, n, with volatile matter (DAF).
Table 8.7 Typical Composition of Mine Dust [14]
Element Weight
Silica 1%e2%
Iron 0.4%
Aluminum 0.98%
Chromium 15.8 ppm
Copper 73.1 ppm
Zinc 312.9 ppm
Cobalt Trace
Carbon The rest
The role of iron sulfate in coal dusteinduced lung injury and injury owing to iron to
proteins in human and rat alveolar microphages have been investigated [17,18]. It ap-
pears that iron may play a bigger role in causing CWP than was realized heretofore.
Finally, one needs to consider the role of free radicals on the respirable dust parti-
cles in the growth of CWP [19]. Freshly cleaved silica and coal particles carry larger
amounts of free radicals as compared with stale or aged particles and are, therefore,
more harmful to lung tissues [20]. Certain water-soluble chemicals, e.g., organosi-
lanes, appear to suppress the free radicals on freshly mined coal, but no experimental
or field data are yet available [21]. It may be easier to remove mine workers away from
the active mine faces by using remote operation to better safeguard their health. This
requires remote operation of all coal cutting and loading equipment.