Page 377 - Advanced Mine Ventilation
P. 377
348 Advanced Mine Ventilation
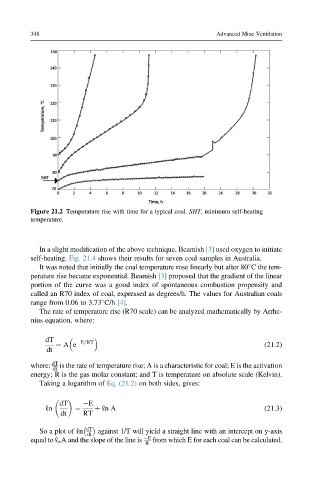
Figure 21.2 Temperature rise with time for a typical coal. SHT, minimum self-heating
temperature.
In a slight modification of the above technique, Beamish [3] used oxygen to initiate
self-heating. Fig. 21.4 shows their results for seven coal samples in Australia.
It was noted that initially the coal temperature rose linearly but after 80 C the tem-
perature rise became exponential. Beamish [3] proposed that the gradient of the linear
portion of the curve was a good index of spontaneous combustion propensity and
called an R70 index of coal, expressed as degrees/h. The values for Australian coals
range from 0.06 to 3.73 C/h [4].
The rate of temperature rise (R70 scale) can be analyzed mathematically by Arrhe-
nius equation, where:
dT E=RT
¼ A e (21.2)
dt
where: dT is the rate of temperature rise; A is a characteristic for coal; E is the activation
dt
energy; R is the gas molar constant; and T is temperature on absolute scale (Kelvin).
Taking a logarithm of Eq. (21.2) on both sides, gives:
dT E
[n ¼ þ [n A (21.3)
dt RT
dT
So a plot of [n against 1/T will yield a straight line with an intercept on y-axis
dt
equal to [ n A and the slope of the line is E from which E for each coal can be calculated.
R