Page 255 - Advances In Productive, Safe, and Responsible Coal Mining
P. 255
234 Advances in Productive, Safe, and Responsible Coal Mining
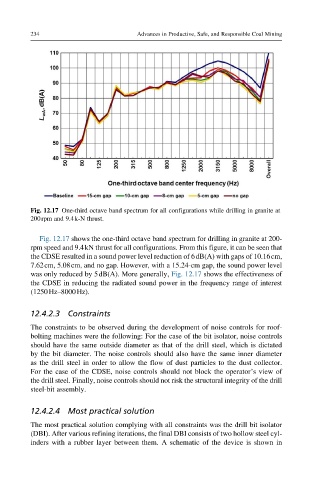
Fig. 12.17 One-third octave band spectrum for all configurations while drilling in granite at
200rpm and 9.4k-N thrust.
Fig. 12.17 shows the one-third octave band spectrum for drilling in granite at 200-
rpm speed and 9.4kN thrust for all configurations. From this figure, it can be seen that
the CDSE resulted in a sound power level reduction of 6dB(A) with gaps of 10.16cm,
7.62cm, 5.08cm, and no gap. However, with a 15.24-cm gap, the sound power level
was only reduced by 5dB(A). More generally, Fig. 12.17 shows the effectiveness of
the CDSE in reducing the radiated sound power in the frequency range of interest
(1250Hz–8000Hz).
12.4.2.3 Constraints
The constraints to be observed during the development of noise controls for roof-
bolting machines were the following: For the case of the bit isolator, noise controls
should have the same outside diameter as that of the drill steel, which is dictated
by the bit diameter. The noise controls should also have the same inner diameter
as the drill steel in order to allow the flow of dust particles to the dust collector.
For the case of the CDSE, noise controls should not block the operator’s view of
the drill steel. Finally, noise controls should not risk the structural integrity of the drill
steel-bit assembly.
12.4.2.4 Most practical solution
The most practical solution complying with all constraints was the drill bit isolator
(DBI). After various refining iterations, the final DBI consists of two hollow steel cyl-
inders with a rubber layer between them. A schematic of the device is shown in