Page 252 - Advances In Productive, Safe, and Responsible Coal Mining
P. 252
Engineered noise controls for miner safety and environmental responsibility 231
110
100
99.2 dBA overall
90
L pA , dB(A) 80
70
60
100 125 160 200 250 315 400 500 630 800 1000 1250 1600 2000 2500 3150 4000 5000 6300 8000 10,000 Overall
One-third octave band center frequency (Hz)
3
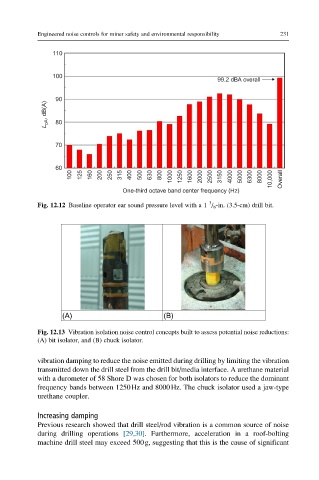
Fig. 12.12 Baseline operator ear sound pressure level with a 1 / 8 -in. (3.5-cm) drill bit.
(A) (B)
Fig. 12.13 Vibration isolation noise control concepts built to assess potential noise reductions:
(A) bit isolator, and (B) chuck isolator.
vibration damping to reduce the noise emitted during drilling by limiting the vibration
transmitted down the drill steel from the drill bit/media interface. A urethane material
with a durometer of 58 Shore D was chosen for both isolators to reduce the dominant
frequency bands between 1250Hz and 8000Hz. The chuck isolator used a jaw-type
urethane coupler.
Increasing damping
Previous research showed that drill steel/rod vibration is a common source of noise
during drilling operations [29,30]. Furthermore, acceleration in a roof-bolting
machine drill steel may exceed 500g, suggesting that this is the cause of significant