Page 36 - Advances in Biomechanics and Tissue Regeneration
P. 36
30 2. BIOMECHANICS OF THE VESTIBULAR SYSTEM: A NUMERICAL SIMULATION
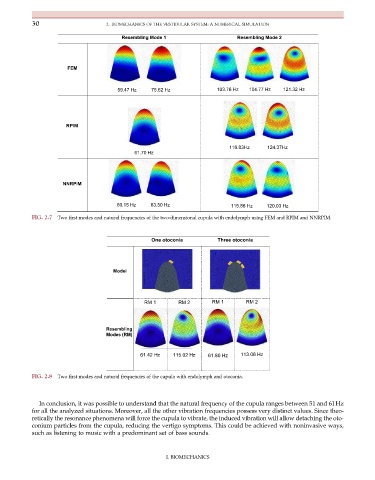
Resembling Mode 1 Resembling Mode 2
FEM
59.47 Hz 75.62 Hz 103.76 Hz 104.77 Hz 121.32 Hz
RPIM
116.83Hz 124.37Hz
61.70 Hz
NNRPIM
60.15 Hz 63.50 Hz 115.86 Hz 120.03 Hz
FIG. 2.7 Two first modes and natural frequencies of the two-dimensional cupula with endolymph using FEM and RPIM and NNRPIM.
One otoconia Three otoconia
Model
RM 1 RM 2 RM 1 RM 2
Resembling
Modes (RM)
61.42 Hz 115.02 Hz 61.80 Hz 113.06 Hz
FIG. 2.8 Two first modes and natural frequencies of the cupula with endolymph and otoconia.
In conclusion, it was possible to understand that the natural frequency of the cupula ranges between 51 and 61Hz
for all the analyzed situations. Moreover, all the other vibration frequencies possess very distinct values. Since theo-
retically the resonance phenomena will force the cupula to vibrate, the induced vibration will allow detaching the oto-
conium particles from the cupula, reducing the vertigo symptoms. This could be achieved with noninvasive ways,
such as listening to music with a predominant set of bass sounds.
I. BIOMECHANICS