Page 257 - Advances in Eco-Fuels for a Sustainable Environment
P. 257
220 Advances in Eco-Fuels for a Sustainable Environment
18
USA-United States of America 2014
16 14.81 15.33 15.8 EU-European Union 2015
14.31 RW-Rest of the World 2016
14 2017
12
Billion gallons 10 8 7.09 7.3 7.06
6 6.19
4
2 1.45 1.39 1.38 1.415 0.875
0.64 0.81 0.85 0.51 0.44 0.44 0.45 0.31 0.33 0.32 0.395 0.16 0.21 0.26 0.31 0.16 0.21 0.23 0.28 0.87 0.39 0.49 0.465
0
USA Brazil EU China Canada Thailand Argentina India RW
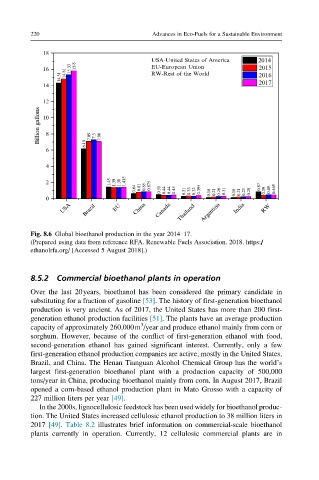
Fig. 8.6 Global bioethanol production in the year 2014–17.
(Prepared using data from reference RFA. Renewable Fuels Association. 2018. https://
ethanolrfa.org/ [Accessed 5 August 2018].)
8.5.2 Commercial bioethanol plants in operation
Over the last 20years, bioethanol has been considered the primary candidate in
substituting for a fraction of gasoline [53]. The history of first-generation bioethanol
production is very ancient. As of 2017, the United States has more than 200 first-
generation ethanol production facilities [51]. The plants have an average production
3
capacity of approximately 260,000m /year and produce ethanol mainly from corn or
sorghum. However, because of the conflict of first-generation ethanol with food,
second-generation ethanol has gained significant interest. Currently, only a few
first-generation ethanol production companies are active, mostly in the United States,
Brazil, and China. The Henan Tianguan Alcohol Chemical Group has the world’s
largest first-generation bioethanol plant with a production capacity of 500,000
tons/year in China, producing bioethanol mainly from corn. In August 2017, Brazil
opened a corn-based ethanol production plant in Mato Grosso with a capacity of
227 million liters per year [49].
In the 2000s, lignocellulosic feedstock has been used widely for bioethanol produc-
tion. The United States increased cellulosic ethanol production to 38 million liters in
2017 [49]. Table 8.2 illustrates brief information on commercial-scale bioethanol
plants currently in operation. Currently, 12 cellulosic commercial plants are in