Page 458 - Advances in Eco-Fuels for a Sustainable Environment
P. 458
Eco friendly biofuels for CI engine applications 411
PSA gas
Water Sulphur Siloxanes
seperation seperation seperation seperation
Biogas system
40%–60% CH CO
4 2
Cooking Natural gas
compressor
Gas 95%–98% CH 4
Cylinders Vehicles
Industrial gas burners
Fig. 15.2 Schematic diagram of conversion of biogas to biomethane (CNG).
Hydrogen is one of the cleanest burning fuels due to its high combustion efficiency
by releasing water vapor during its burning process. Hydrogen can be produced using
synthesis gas or electrolyses. Hydrogen is very efficient as a fuel and has virtually no
throttling losses; it has a clean exhaust with no harmful pollutants such as CO, HC, or
PAHs. The only obstacle for commercialization of hydrogen for internal combustion
engine applications is the lack of storage and supply infrastructure because of its short
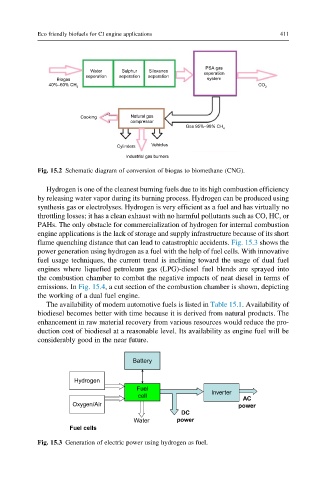
flame quenching distance that can lead to catastrophic accidents. Fig. 15.3 shows the
power generation using hydrogen as a fuel with the help of fuel cells. With innovative
fuel usage techniques, the current trend is inclining toward the usage of dual fuel
engines where liquefied petroleum gas (LPG)-diesel fuel blends are sprayed into
the combustion chamber to combat the negative impacts of neat diesel in terms of
emissions. In Fig. 15.4, a cut section of the combustion chamber is shown, depicting
the working of a dual fuel engine.
The availability of modern automotive fuels is listed in Table 15.1. Availability of
biodiesel becomes better with time because it is derived from natural products. The
enhancement in raw material recovery from various resources would reduce the pro-
duction cost of biodiesel at a reasonable level. Its availability as engine fuel will be
considerably good in the near future.
Battery
Hydrogen
Fuel
Inverter
cell
AC
Oxygen/Air power
DC
Water power
Fuel cells
Fig. 15.3 Generation of electric power using hydrogen as fuel.