Page 246 - Advances in Forensic Applications of Mass Spectrometry - Jehuda Yinon
P. 246
1522_book.fm Page 219 Thursday, November 13, 2003 9:58 AM
kCount GC/MS Spectra
2.0 Stair Tread - GC/MS Scan 1161 from d:\data0199\file4886.msSpect 1
1.5 1317.234 min. Scan: 1161 Chan: 1 Ion: 46 us RIC: 7979382
100%
1.0 Would be Negative
75%
0.5
*
0.0
MCount 50% Co-elutants
Gasoline - GC/MS
0.7 * Poor comparability 146
25% 91
115
0.5 41 51
105 160
69 77
1 1
0.2 50 75 100 125 150 175 m/z
0.0 GC/MS/MS
kCount Daughter Ion Spectra
Stair Tread - GC/MS/MS
3 Confirmed Positive Scan 350 from d:\data0999\f5704ms
2.msSpect 1BP 131 (2642=100%)
2 100% Scan: 350 Chan: 1 Ion: NA RIC: 111587.243 min.
19
Clean & Isomer
1 75% Specific
0 **
kCount 50%
70 Gasoline - GC/MS/MS **
60 Excellent comparison 105
50
40 25%
30 91 145
20
10 50 75 100 125 150 175 m/z
0 New Spectra = Additional
4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 minutes
Identification Assurance
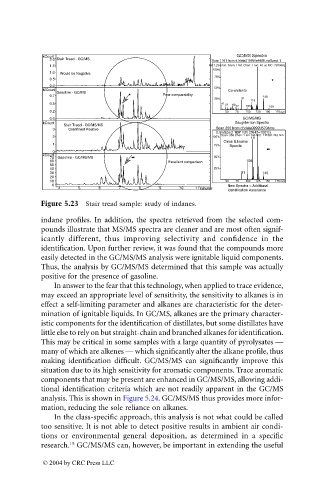
Figure 5.23 Stair tread sample: study of indanes.
indane profiles. In addition, the spectra retrieved from the selected com-
pounds illustrate that MS/MS spectra are cleaner and are most often signif-
icantly different, thus improving selectivity and confidence in the
identification. Upon further review, it was found that the compounds more
easily detected in the GC/MS/MS analysis were ignitable liquid components.
Thus, the analysis by GC/MS/MS determined that this sample was actually
positive for the presence of gasoline.
In answer to the fear that this technology, when applied to trace evidence,
may exceed an appropriate level of sensitivity, the sensitivity to alkanes is in
effect a self-limiting parameter and alkanes are characteristic for the deter-
mination of ignitable liquids. In GC/MS, alkanes are the primary character-
istic components for the identification of distillates, but some distillates have
little else to rely on but straight-chain and branched alkanes for identification.
This may be critical in some samples with a large quantity of pyrolysates —
many of which are alkenes — which significantly alter the alkane profile, thus
making identification difficult. GC/MS/MS can significantly improve this
situation due to its high sensitivity for aromatic components. Trace aromatic
components that may be present are enhanced in GC/MS/MS, allowing addi-
tional identification criteria which are not readily apparent in the GC/MS
analysis. This is shown in Figure 5.24. GC/MS/MS thus provides more infor-
mation, reducing the sole reliance on alkanes.
In the class-specific approach, this analysis is not what could be called
too sensitive. It is not able to detect positive results in ambient air condi-
tions or environmental general deposition, as determined in a specific
15
research. GC/MS/MS can, however, be important in extending the useful
© 2004 by CRC Press LLC