Page 251 - Advances in Renewable Energies and Power Technologies
P. 251
224 CHAPTER 6 Flexible Power Control of Photovoltaic Systems
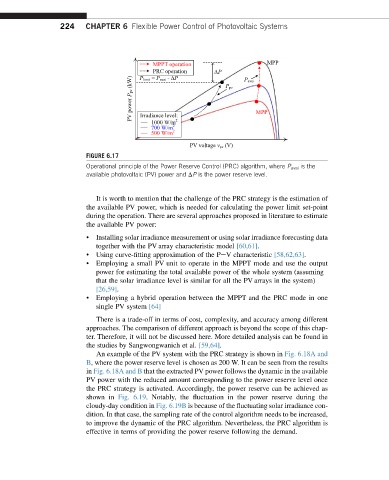
MPPT operation MPP
PRC operation ∆P
(kW) P limit = P avai -∆P P pv P avai
P pv
power
PV Irradiance level: MPP
1000 W/m 2
700 W/m 2
500 W/m 2
PV voltage v pv (V)
FIGURE 6.17
Operational principle of the Power Reserve Control (PRC) algorithm, where P avai is the
available photovoltaic (PV) power and DP is the power reserve level.
It is worth to mention that the challenge of the PRC strategy is the estimation of
the available PV power, which is needed for calculating the power limit set-point
during the operation. There are several approaches proposed in literature to estimate
the available PV power:
• Installing solar irradiance measurement or using solar irradiance forecasting data
together with the PV array characteristic model [60,61].
• Using curve-fitting approximation of the PeV characteristic [58,62,63].
• Employing a small PV unit to operate in the MPPT mode and use the output
power for estimating the total available power of the whole system (assuming
that the solar irradiance level is similar for all the PV arrays in the system)
[26,59].
• Employing a hybrid operation between the MPPT and the PRC mode in one
single PV system [64]
There is a trade-off in terms of cost, complexity, and accuracy among different
approaches. The comparison of different approach is beyond the scope of this chap-
ter. Therefore, it will not be discussed here. More detailed analysis can be found in
the studies by Sangwongwanich et al. [59,64].
An example of the PV system with the PRC strategy is shown in Fig. 6.18A and
B, where the power reserve level is chosen as 200 W. It can be seen from the results
in Fig. 6.18A and B that the extracted PV power follows the dynamic in the available
PV power with the reduced amount corresponding to the power reserve level once
the PRC strategy is activated. Accordingly, the power reserve can be achieved as
shown in Fig. 6.19. Notably, the fluctuation in the power reserve during the
cloudy-day condition in Fig. 6.19B is because of the fluctuating solar irradiance con-
dition. In that case, the sampling rate of the control algorithm needs to be increased,
to improve the dynamic of the PRC algorithm. Nevertheless, the PRC algorithm is
effective in terms of providing the power reserve following the demand.