Page 238 - Air Pollution Control Engineering
P. 238
05_chap_wang.qxd 05/05/2004 3:46 pm Page 217
Wet and Dry Scrubbing 217
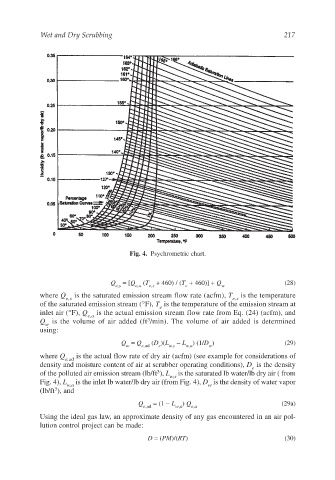
Fig. 4. Psychrometric chart.
Q = [Q (T + 460) / (T + 460)] + Q (28)
e,s e,a e,s e w
where Q is the saturated emission stream flow rate (acfm), T is the temperature
e,s e,s
of the saturated emission stream (°F), T is the temperature of the emission stream at
e
inlet air (°F), Q is the actual emission stream flow rate from Eq. (24) (acfm), and
e,a
3
Q is the volume of air added (ft /min). The volume of air added is determined
w
using:
Q = Q (D )(L − L ) (1/D ) (29)
w e,ad e w,s w,a w
where Q is the actual flow rate of dry air (acfm) (see example for considerations of
e,ad
density and moisture content of air at scrubber operating conditions), D is the density
e
3
of the polluted air emission stream (lb/ft ), L is the saturated lb water/lb dry air ( from
w,s
Fig. 4), L is the inlet lb water/lb dry air (from Fig. 4), D is the density of water vapor
w,a w
3
(lb/ft ), and
Q = (1 − L ) Q (29a)
e,ad w,a e,a
Using the ideal gas law, an approximate density of any gas encountered in an air pol-
lution control project can be made:
D = (PM)/(RT) (30)