Page 261 - Air Pollution Control Engineering
P. 261
05_chap_wang.qxd 05/05/2004 3:46 pm Page 240
240 Lawrence K. Wang et al.
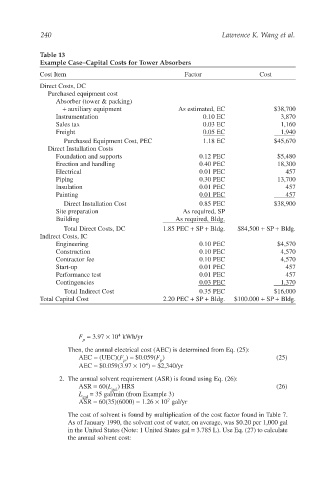
Table 13
Example Case–Capital Costs for Tower Absorbers
Cost Item Factor Cost
Direct Costs, DC
Purchased equipment cost
Absorber (tower & packing)
+ auxiliary equipment As estimated, EC $38,700
Instrumentation 0.10 EC 3,870
Sales tax 0.03 EC 1,160
Freight 0.05 EC 1,940
Purchased Equipment Cost, PEC 1.18 EC $45,670
Direct Installation Costs
Foundation and supports 0.12 PEC $5,480
Erection and handling 0.40 PEC 18,300
Electrical 0.01 PEC 457
Piping 0.30 PEC 13,700
Insulation 0.01 PEC 457
Painting 0.01 PEC 457
Direct Installation Cost 0.85 PEC $38,900
Site preparation As required, SP
Building As required, Bldg.
Total Direct Costs, DC 1.85 PEC + SP + Bldg. $84,500 + SP + Bldg.
Indirect Costs, IC
Engineering 0.10 PEC $4,570
Construction 0.10 PEC 4,570
Contractor fee 0.10 PEC 4,570
Start-up 0.01 PEC 457
Performance test 0.01 PEC 457
Contingencies 0.03 PEC 1,370
Total Indirect Cost 0.35 PEC $16,000
Total Capital Cost 2.20 PEC + SP + Bldg. $100.000 + SP + Bldg.
4
F = 3.97 × 10 kWh/yr
p
Then, the annual electrical cost (AEC) is determined from Eq. (25):
AEC = (UEC)(F ) = $0.059(F ) (25)
p p
4
AEC = $0.059(3.97 × 10 ) = $2,340/yr
2. The annual solvent requirement (ASR) is found using Eq. (26):
ASR = 60(L ) HRS (26)
gal
L = 35 gal/min (from Example 3)
gal
7
ASR = 60(35)(6000) = 1.26 × 10 gal/yr
The cost of solvent is found by multiplication of the cost factor found in Table 7.
As of January 1990, the solvent cost of water, on average, was $0.20 per 1,000 gal
in the United States (Note: 1 United States gal = 3.785 L). Use Eq. (27) to calculate
the annual solvent cost: