Page 408 - Air Pollution Control Engineering
P. 408
09_chap_wang.qxd 05/05/2004 5:01 pm Page 381
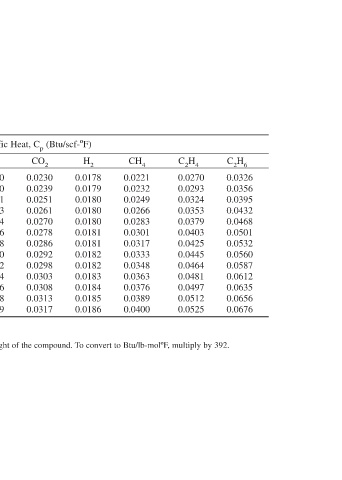
C 2 H 6 0.0326 0.0356 0.0395 0.0432 0.0468 0.0501 0.0532 0.0560 0.0587 0.0612 0.0635 0.0656 0.0676
C 2 H 4 0.0270 0.0293 0.0324 0.0353 0.0379 0.0403 0.0425 0.0445 0.0464 0.0481 0.0497 0.0512 0.0525
CH 4 0.0221 0.0232 0.0249 0.0266 0.0283 0.0301 0.0317 0.0333 0.0348 0.0363 0.0376 0.0389 0.0400
(Btu/scf-ºF) H 2 CO 2 0.0178 0.0230 0.0179 0.0239 0.0180 0.0251 0.0180 0.0261 0.0180 0.0270 0.0181 0.0278 0.0181 0.0286 0.0182 0.0292 0.0182 0.0298 0.0183 0.0303 0.0184 0.0308 0.0185 0.0313 0.0186 0.0317
Average Specific Heat, C p CO 0.0180 0.0180 0.0181 0.0183 0.0184 0.0186 0.0188 0.0190 0.0192 0.0194 0.0196 0.0198 0.0199 To convert to Btu/lb-ºF basis, multiply by 392 and divide by the molecular weight of the compound. To convert to Btu/lb-molºF, multiply by 392.
0.0181 0.0207 0.0183 0.0209 0.0186 0.0211 0.0188 0.0212 0.0191 0.0217 0.0194 0.0221 0.0197 0.0224 0.0228 0.0232 0.0235 0.0239 0.0243 0.0208 0.0246 Note: Average for the temperature interval 77ºF and the specified temperature.
O 2 N 2 0.0180 0.0180 0.0181 0.0182 0.0183 0.0185 0.0187 0.0189 0.0199 0.0190 0.0201 0.0192 0.0203 0.0194 0.0205 0.0196 0.0207 0.0197
Average Specific Heats of Vapors Air 0.0180 0.0180 0.0181 0.0183 0.0185 0.0187 0.0189 0.0191 0.0192 0.0194 0.0196 0.0198 0.0199 Based on 70ºF and 1 atm
H 2 O
Table 5 Temperature (ºF) 77 212 392 572 752 932 1112 1292 1472 1652 1832 2012 2192 Source: ref. 4.
381