Page 148 - Air pollution and greenhouse gases from basic concepts to engineering applications for air emission control
P. 148
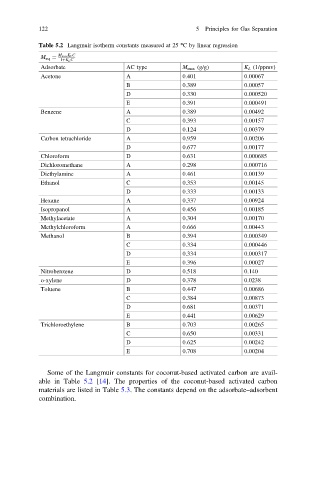
122 5 Principles for Gas Separation
Table 5.2 Langmuir isotherm constants measured at 25 °C by linear regression
M max K L C
M eq ¼
1þK L C
Adsorbate AC type M max (g/g) K L (1/ppmv)
Acetone A 0.401 0.00067
B 0.389 0.00057
D 0.330 0.000520
E 0.391 0.000491
Benzene A 0.389 0.00492
C 0.393 0.00157
D 0.124 0.00379
Carbon tetrachloride A 0.959 0.00206
D 0.677 0.00177
Chloroform D 0.631 0.000685
Dichloromethane A 0.298 0.000716
Diethylamine A 0.461 0.00139
Ethanol C 0.353 0.00145
D 0.333 0.00133
Hexane A 0.337 0.00924
Isopropanol A 0.456 0.00185
Methylacetate A 0.304 0.00170
Methylchloroform A 0.666 0.00443
Methanol B 0.394 0.000349
C 0.334 0.000446
D 0.334 0.000317
E 0.396 0.00027
Nitrobenzene D 0.518 0.140
o-xylene D 0.378 0.0238
Toluene B 0.447 0.00686
C 0.384 0.00873
D 0.681 0.00371
E 0.441 0.00629
Trichloroethylene B 0.703 0.00265
C 0.650 0.00331
D 0.625 0.00242
E 0.708 0.00204
Some of the Langmuir constants for coconut-based activated carbon are avail-
able in Table 5.2 [14]. The properties of the coconut-based activated carbon
materials are listed in Table 5.3. The constants depend on the adsorbate–adsorbent
combination.