Page 158 - Air pollution and greenhouse gases from basic concepts to engineering applications for air emission control
P. 158
132 5 Principles for Gas Separation
wave can be determined by similar analysis. Readers are referred to the literature for
in-depth analysis.
5.2 Absorption
Absorption is a volumetric process where gases penetrate into the structure of the
solid or liquid, most likely by diffusion. Similar to the classification of adsorption,
absorption can also be classified into physioabsorption and chemioabsorption. A
physioabsorption involves negligible chemical reactions, for example solution of
oxygen in water. The physical absorption process involves a mass transfer by means
of molecular and turbulent diffusion governed by Henry’s law (see Sect. 2.3.1).
A chemioabsorption process results in new substances from the chemical reactions.
For example, when a flue gas passes through a water spray, the droplets will capture
the gaseous SO 2 molecules by absorption. Captured SO 2 molecules dissolve in the
body of a water droplet and produces H 2 SO 3 .
An absorption-based process is also commonly referred to as wet scrubbing.
However, one has to be careful that wet scrubbing of particles is based on the
principles of impaction and coagulation, whereas wet scrubbing of gaseous pol-
lutants is based on absorption. In this section, we explain the basics using counter
flow absorption tower.
5.2.1 Counter Flow Absorption Tower
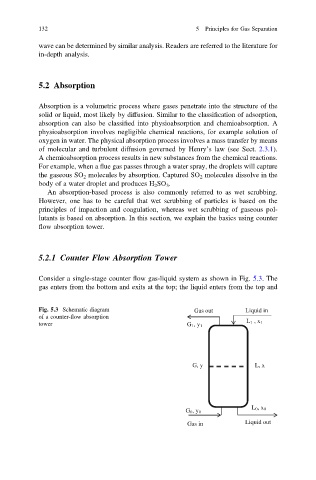
Consider a single-stage counter flow gas-liquid system as shown in Fig. 5.3. The
gas enters from the bottom and exits at the top; the liquid enters from the top and
Fig. 5.3 Schematic diagram Gas out Liquid in
of a counter-flow absorption
tower G 1,y 1 L 1 , x 1
G, y L, x
L 0, x 0
G 0, y 0
Gas in Liquid out