Page 348 - Air pollution and greenhouse gases from basic concepts to engineering applications for air emission control
P. 348
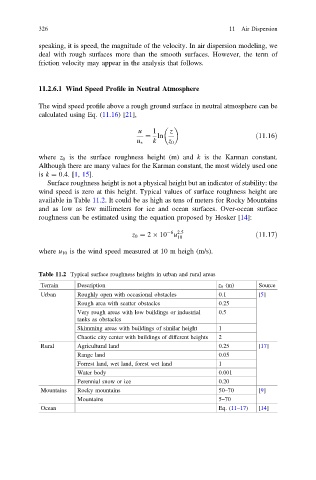
326 11 Air Dispersion
speaking, it is speed, the magnitude of the velocity. In air dispersion modeling, we
deal with rough surfaces more than the smooth surfaces. However, the term of
friction velocity may appear in the analysis that follows.
11.2.6.1 Wind Speed Profile in Neutral Atmosphere
The wind speed profile above a rough ground surface in neutral atmosphere can be
calculated using Eq. (11.16)[21],
u 1 z
¼ ln ð11:16Þ
k
u z 0
where z 0 is the surface roughness height (m) and k is the Karman constant.
Although there are many values for the Karman constant, the most widely used one
is k ¼ 0:4. [1, 15].
Surface roughness height is not a physical height but an indicator of stability: the
wind speed is zero at this height. Typical values of surface roughness height are
available in Table 11.2. It could be as high as tens of meters for Rocky Mountains
and as low as few millimeters for ice and ocean surfaces. Over-ocean surface
roughness can be estimated using the equation proposed by Hosker [14]:
6 2:5
z 0 ¼ 2 10 u 10 ð11:17Þ
where u 10 is the wind speed measured at 10 m heigh (m/s).
Table 11.2 Typical surface roughness heights in urban and rural areas
Terrain Description z 0 (m) Source
Urban Roughly open with occasional obstacles 0.1 [5]
Rough area with scatter obstacles 0.25
Very rough areas with low buildings or industrial 0.5
tanks as obstacles
Skimming areas with buildings of similar height 1
Chaotic city center with buildings of different heights 2
Rural Agricultural land 0.25 [17]
Range land 0.05
Forrest land, wet land, forest wet land 1
Water body 0.001
Perennial snow or ice 0.20
Mountains Rocky mountains 50–70 [9]
Mountains 5–70
Ocean Eq. (11–17) [14]