Page 352 - Air pollution and greenhouse gases from basic concepts to engineering applications for air emission control
P. 352
330 11 Air Dispersion
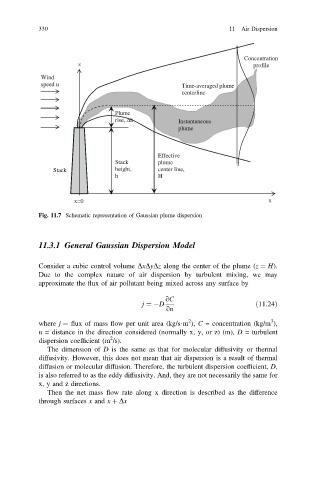
Concentration
z profile
Wind
speed u Time-averaged plume
centerline
Plume
rise, Δh Instantaneous
plume
Effective
Stack plume
Stack height, center line,
h H
x=0 x
Fig. 11.7 Schematic representation of Gaussian plume dispersion
11.3.1 General Gaussian Dispersion Model
Consider a cubic control volume DxDyDz along the center of the plume (z ¼ H).
Due to the complex nature of air dispersion by turbulent mixing, we may
approximate the flux of air pollutant being mixed across any surface by
oC
j ¼ D ð11:24Þ
on
2
3
where j ¼ flux of mass flow per unit area (kg/s·m ), C = concentration (kg/m ),
n = distance in the direction considered (normally x, y, or z) (m), D = turbulent
2
dispersion coefficient (m /s).
The dimension of D is the same as that for molecular diffusivity or thermal
diffusivity. However, this does not mean that air dispersion is a result of thermal
diffusion or molecular diffusion. Therefore, the turbulent dispersion coefficient, D,
is also referred to as the eddy diffusivity. And, they are not necessarily the same for
x, y and z directions.
Then the net mass flow rate along x direction is described as the difference
through surfaces x and x þ Dx