Page 392 - Air pollution and greenhouse gases from basic concepts to engineering applications for air emission control
P. 392
12.6 CO 2 Separation by Absorption 371
0
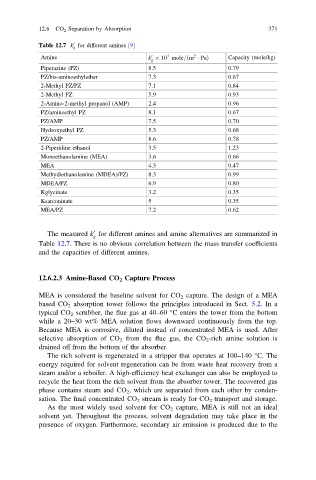
Table 12.7 k for different amines [9]
g
7
Amine k 10 mole= m Pað 2 Þ Capacity (mole/kg)
0
g
Piperazine (PZ) 8.5 0.79
PZ/bis-aminoethylether 7.3 0.67
2-Methyl PZ/PZ 7.1 0.84
2-Methyl PZ 5.9 0.93
2-Amino-2-methyl propanol (AMP) 2.4 0.96
PZ/aminoethyl PZ 8.1 0.67
PZ/AMP 7.5 0.70
Hydroxyethyl PZ 5.3 0.68
PZ/AMP 8.6 0.78
2-Piperidine ethanol 3.5 1.23
Monoethanolamine (MEA) 3.6 0.66
MEA 4.3 0.47
Methydiethanolamine (MDEA)/PZ) 8.3 0.99
MDEA/PZ 6.9 0.80
Kglycinate 3.2 0.35
Ksarconinate 5 0.35
MEA/PZ 7.2 0.62
0
The measured k for different amines and amine alternatives are summarized in
g
Table 12.7. There is no obvious correlation between the mass transfer coefficients
and the capacities of different amines.
12.6.2.3 Amine-Based CO 2 Capture Process
MEA is considered the baseline solvent for CO 2 capture. The design of a MEA
based CO 2 absorption tower follows the principles introduced in Sect. 5.2.Ina
typical CO 2 scrubber, the flue gas at 40–60 °C enters the tower from the bottom
while a 20–30 wt% MEA solution flows downward continuously from the top.
Because MEA is corrosive, diluted instead of concentrated MEA is used. After
selective absorption of CO 2 from the flue gas, the CO 2 -rich amine solution is
drained off from the bottom of the absorber.
The rich solvent is regenerated in a stripper that operates at 100–140 °C. The
energy required for solvent regeneration can be from waste heat recovery from a
steam and/or a reboiler. A high-efficiency heat exchanger can also be employed to
recycle the heat from the rich solvent from the absorber tower. The recovered gas
phase contains steam and CO 2 , which are separated from each other by conden-
sation. The final concentrated CO 2 stream is ready for CO 2 transport and storage.
As the most widely used solvent for CO 2 capture, MEA is still not an ideal
solvent yet. Throughout the process, solvent degradation may take place in the
presence of oxygen. Furthermore, secondary air emission is produced due to the