Page 388 - Air pollution and greenhouse gases from basic concepts to engineering applications for air emission control
P. 388
12.6 CO 2 Separation by Absorption 367
12.6.2 Amine-Based Chemical Absorption
Chemical absorption is suitable for CO 2 capture at low pressure and low temper-
ature. The sorbents used for chemical absorption include carbonate-based, sodium
hydroxide-based, aqueous ammonia-based, and amine-based sorbents.
Amine-based CO 2 absorption is a relatively mature technology used in the
ammonia process, steam reforming process, and the natural gas sweetening process.
Amines are ammonia-derived organic compounds when one or more hydrogen
atom(s) of ammonia are replaced with organic substituents. Amines are classified as
primary, secondary, and tertiary amines based on the number of replaced hydrogen
atoms.
The choice of amine for CO 2 absorption depends on three key factors: rate of
reaction, regeneration energy, and loading capacity. The ideal solvent is characterized
with a great rate of reaction, low regeneration energy, and great loading capacity.
However, none of the alkanolamines meets all these three requirements. In general,
the rate of reaction follows the order of primary > secondary > tertiary; the order is
reversed for regeneration energy and loading capacity [35]. Ethanolamine (C 2 H 7 NO
or 2R-NH 2 ), also called 2-aminoethanol or monoethanolamine (MEA) is the most
commonly used amine for CO 2 absorption. It is a primary amine, and a alcohol too.
Among all the amines tested, MEA showed its high reactivity with CO 2 , and is
predominantly used for CO 2 capture in the industry. Aqueous amine solutions are
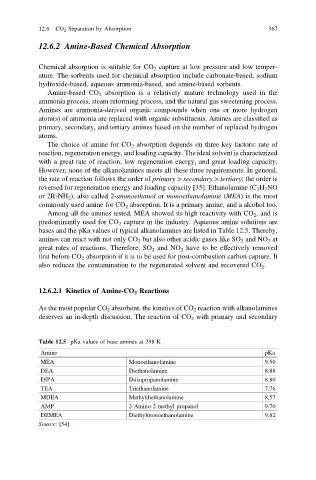
bases and the pKa values of typical alkanolamines are listed in Table 12.5. Thereby,
amines can react with not only CO 2 but also other acidic gases like SO 2 and NO 2 at
great rates of reactions. Therefore, SO 2 and NO 2 have to be effectively removed
first before CO 2 absorption if it is to be used for post-combustion carbon capture. It
also reduces the contamination to the regenerated solvent and recovered CO 2 .
12.6.2.1 Kinetics of Amine-CO 2 Reactions
As the most popular CO 2 absorbent, the kinetics of CO 2 reaction with alkanolamines
deserves an in-depth discussion. The reaction of CO 2 with primary and secondary
Table 12.5 pKa values of base amines at 298 K
Amine pKa
MEA Monoethanolamine 9.50
DEA Diethanolamine 8.88
DIPA Diisopropanolamine 8.80
TEA Triethanolamine 7.76
MDEA Methyldiethanolamine 8.57
AMP 2-Amino-2-methyl propanol 9.70
DEMEA Diethylmonoethanolamine 9.82
Source:[54]