Page 385 - Air pollution and greenhouse gases from basic concepts to engineering applications for air emission control
P. 385
364 12 Carbon Capture and Storage
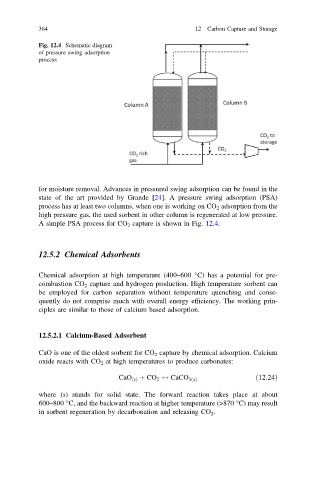
Fig. 12.4 Schematic diagram
of pressure swing adsorption
process
for moisture removal. Advances in pressured swing adsorption can be found in the
state of the art provided by Grande [24]. A pressure swing adsorption (PSA)
process has at least two columns, when one is working on CO 2 adsorption from the
high pressure gas, the used sorbent in other column is regenerated at low pressure.
A simple PSA process for CO 2 capture is shown in Fig. 12.4.
12.5.2 Chemical Adsorbents
Chemical adsorption at high temperature (400–600 °C) has a potential for pre-
combustion CO 2 capture and hydrogen production. High temperature sorbent can
be employed for carbon separation without temperature quenching and conse-
quently do not comprise much with overall energy efficiency. The working prin-
ciples are similar to those of calcium based adsorption.
12.5.2.1 Calcium-Based Adsorbent
CaO is one of the oldest sorbent for CO 2 capture by chemical adsorption. Calcium
oxide reacts with CO 2 at high temperatures to produce carbonates:
ð12:24Þ
CaO sðÞ þ CO 2 $ CaCO 3 sðÞ
where (s) stands for solid state. The forward reaction takes place at about
600–800 °C, and the backward reaction at higher temperature (>870 °C) may result
in sorbent regeneration by decarbonation and releasing CO 2 .