Page 381 - Air pollution and greenhouse gases from basic concepts to engineering applications for air emission control
P. 381
360 12 Carbon Capture and Storage
Although it is only estimation, the comparison does show that the oxyfuel
combustion flame temperature is higher than that of conventional combustion with
air. As a result, the boiler of the oxyfuel combustion process requires special
materials that can survive extreme temperature.
Another concern of the oxyfuel combustion process with sulfur containing fuels
is the high SO x concentration without the dilution of nitrogen, resulting in high
corrosion on the ducts. Extra costs are associated with concentrated oxygen pro-
duction by costly air separation units.
The benefit is a simple process for carbon capture after combustion. Without
nitrogen and NO x in the flue gas, it contains mainly H 2 O and CO 2 . After the
removal of soot and SO 2 , if any, CO 2 can be readily separated from water vapor by
condensation in a cooler. This highly concentrated CO 2 is ready for transportation
and storage.
12.4.2.2 Chemical Looping Combustion
Similar to oxyfuel combustion, chemical-looping combustion is an emerging
combustion process that is attractive for the benefit of carbon capture. This idea was
first introduced by Lewis and Gilliland [38] as a way to produce pure CO 2 from
fossil fuels. Thirty years later, Ishida et al. [33] proposed the use of chemical-
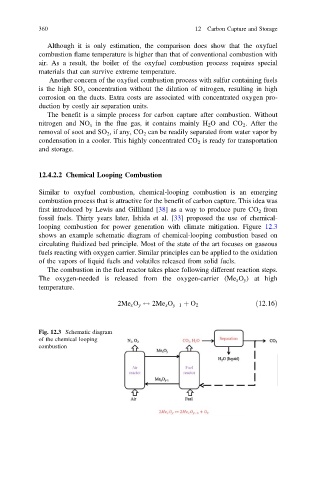
looping combustion for power generation with climate mitigation. Figure 12.3
shows an example schematic diagram of chemical-looping combustion based on
circulating fluidized bed principle. Most of the state of the art focuses on gaseous
fuels reacting with oxygen carrier. Similar principles can be applied to the oxidation
of the vapors of liquid fuels and volatiles released from solid fuels.
The combustion in the fuel reactor takes place following different reaction steps.
The oxygen-needed is released from the oxygen-carrier (Me x O y ) at high
temperature.
2Me x O y $ 2Me x O y 1 þ O 2 ð12:16Þ
Fig. 12.3 Schematic diagram
of the chemical looping
combustion