Page 377 - Air pollution and greenhouse gases from basic concepts to engineering applications for air emission control
P. 377
356 12 Carbon Capture and Storage
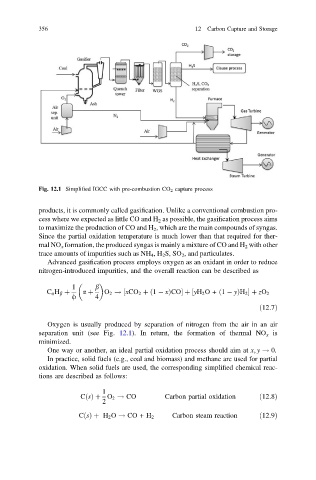
Fig. 12.1 Simplified IGCC with pre-combustion CO 2 capture process
products, it is commonly called gasification. Unlike a conventional combustion pro-
cess where we expected as little CO and H 2 as possible, the gasification process aims
to maximize the production of CO and H 2 , which are the main compounds of syngas.
Since the partial oxidation temperature is much lower than that required for ther-
mal NO x formation, the produced syngas is mainly a mixture of CO and H 2 with other
trace amounts of impurities such as NH 4 ,H 2 S, SO 2 , and particulates.
Advanced gasification process employs oxygen as an oxidant in order to reduce
nitrogen-introduced impurities, and the overall reaction can be described as
1 b
ð
½
C a H b þ a þ O 2 ! xCO 2 þ 1 xð½ ÞCO þ yH 2 O+ 1 yÞH 2 þ zO 2
/ 4
ð12:7Þ
Oxygen is usually produced by separation of nitrogen from the air in an air
separation unit (see Fig. 12.1). In return, the formation of thermal NO x is
minimized.
One way or another, an ideal partial oxidation process should aim at x; y ! 0.
In practice, solid fuels (e.g., coal and biomass) and methane are used for partial
oxidation. When solid fuels are used, the corresponding simplified chemical reac-
tions are described as follows:
1
C sðÞ þ O 2 ! CO Carbon partial oxidation ð12:8Þ
2
C sðÞ þ H 2 O ! CO + H 2 Carbon steam reaction ð12:9Þ