Page 374 - Air pollution and greenhouse gases from basic concepts to engineering applications for air emission control
P. 374
12.2 CO 2 Generation in Combustion 353
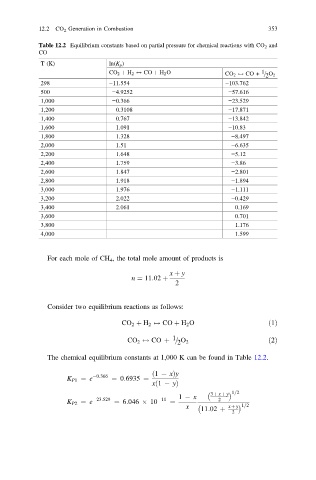
Table 12.2 Equilibrium constants based on partial pressure for chemical reactions with CO 2 and
CO
T (K) ln(K p )
CO 2 þ H 2 $ CO þ H 2 O 1
2
CO 2 $ CO + = O 2
298 −11.554 −103.762
500 −4.9252 −57.616
1,000 −0.366 −23.529
1,200 0.3108 −17.871
1,400 0.767 −13.842
1,600 1.091 −10.83
1,800 1.328 −8.497
2,000 1.51 −6.635
2,200 1.648 −5.12
2,400 1.759 −3.86
2,600 1.847 −2.801
2,800 1.918 −1.894
3,000 1.976 −1.111
3,200 2.022 −0.429
3,400 2.061 0.169
3,600 0.701
3,800 1.176
4,000 1.599
For each mole of CH 4 , the total mole amount of products is
x þ y
n ¼ 11:02 þ
2
Consider two equilibrium reactions as follows:
CO 2 þ H 2 $ CO þ H 2 O ð1Þ
1
2
CO 2 $ CO þ = O 2 ð2Þ
The chemical equilibrium constants at 1,000 K can be found in Table 12.2.
ð1 xÞy
0:366
K P1 ¼ e ¼ 0:6935 ¼
xð1 yÞ
3 þ x þ y 1=2
1 x 2
23:529
11
K P2 ¼ e ¼ 6:046 10 ¼
x x þ y 1=2
11:02 þ
2