Page 379 - Air pollution and greenhouse gases from basic concepts to engineering applications for air emission control
P. 379
358 12 Carbon Capture and Storage
12.4.2 In-combustion Carbon Capture
12.4.2.1 Oxyfuel Combustion
In-combustion carbon capture is achieved primarily by oxyfuel combustion. Oxy-
gen rather than air is used as oxidizer in combustion. Then the main combustion
products, as described using Eq. (12.2), are CO 2 and water. Depending on the fuel
composition, there may be SO 2 ,NO x and others, but thermal NO x is greatly
reduced. As a result, the CO 2 can be readily separated from water and other trace
compounds for transport and storage.
The oxyfuel combustion process is a promising concept but still under research
and development (R&D). The fuels fed into an oxyfuel combustion system can be
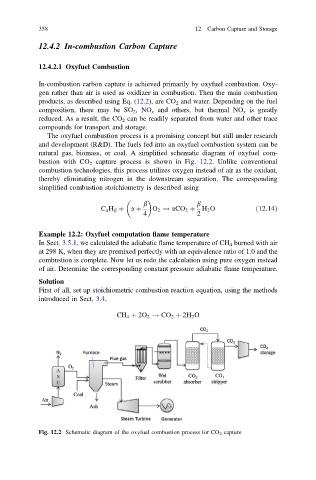
natural gas, biomass, or coal. A simplified schematic diagram of oxyfuel com-
bustion with CO 2 capture process is shown in Fig. 12.2. Unlike conventional
combustion technologies, this process utilizes oxygen instead of air as the oxidant,
thereby eliminating nitrogen in the downstream separation. The corresponding
simplified combustion stoichiometry is described using
b b
C a H b þ a þ O 2 ! aCO 2 þ H 2 O ð12:14Þ
4 2
Example 12.2: Oxyfuel computation flame temperature
In Sect. 3.5.1, we calculated the adiabatic flame temperature of CH 4 burned with air
at 298 K, when they are premixed perfectly with an equivalence ratio of 1.0 and the
combustion is complete. Now let us redo the calculation using pure oxygen instead
of air. Determine the corresponding constant pressure adiabatic flame temperature.
Solution
First of all, set up stoichiometric combustion reaction equation, using the methods
introduced in Sect. 3.4,
CH 4 þ 2O 2 ! CO 2 þ 2H 2 O
Fig. 12.2 Schematic diagram of the oxyfuel combustion process for CO 2 capture