Page 386 - Air pollution and greenhouse gases from basic concepts to engineering applications for air emission control
P. 386
12.5 CO 2 Separation by Adsorption 365
Calcium-based sorbents are commonly produced from limestone. Sometimes,
sorbents that are produced from calcined dolomite (CaCO 3 MgCO ) or huntite
3
(CaCO 3 3MgCO ) contain MgO. MgO does not react with CO 2 at 600–800 °C,
3
but its presence helps with the lifetime and durability of the calcium-based sorbent.
Since CaO degrades quickly after a few cycles of regeneration, more reliable sor-
bents have been developed and tested at high temperatures; they include Calcium
aluminate (CaAl 2 O 4 ), Sodium Zirconate (Na 2 ZrO 3 ), Lithium zircanate (Li 2 ZrO 3 ),
and Lithium orthosilicate (Li 4 SiO 4 ).
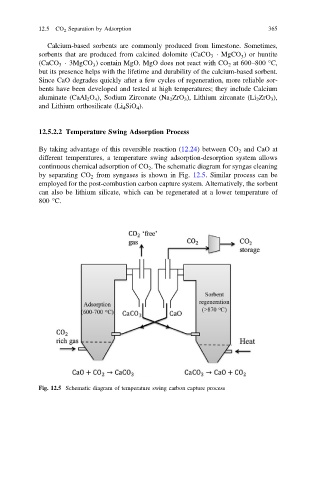
12.5.2.2 Temperature Swing Adsorption Process
By taking advantage of this reversible reaction (12.24) between CO 2 and CaO at
different temperatures, a temperature swing adsorption-desorption system allows
continuous chemical adsorption of CO 2 . The schematic diagram for syngas cleaning
by separating CO 2 from syngases is shown in Fig. 12.5. Similar process can be
employed for the post-combustion carbon capture system. Alternatively, the sorbent
can also be lithium silicate, which can be regenerated at a lower temperature of
800 °C.
Fig. 12.5 Schematic diagram of temperature swing carbon capture process