Page 469 - Air pollution and greenhouse gases from basic concepts to engineering applications for air emission control
P. 469
450 15 Air Monitoring
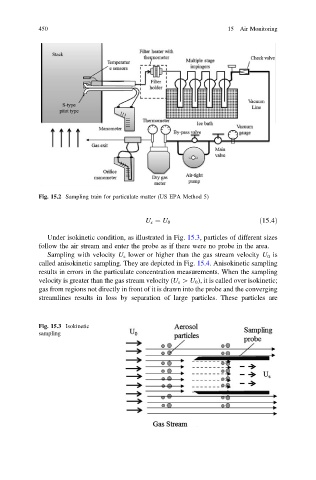
Fig. 15.2 Sampling train for particulate matter (US EPA Method 5)
U s ¼ U 0 ð15:4Þ
Under isokinetic condition, as illustrated in Fig. 15.3, particles of different sizes
follow the air stream and enter the probe as if there were no probe in the area.
Sampling with velocity U s lower or higher than the gas stream velocity U 0 is
called anisokinetic sampling. They are depicted in Fig. 15.4. Anisokinetic sampling
results in errors in the particulate concentration measurements. When the sampling
velocity is greater than the gas stream velocity (U s [ U 0 ), it is called over isokinetic;
gas from regions not directly in front of it is drawn into the probe and the converging
streamlines results in loss by separation of large particles. These particles are
Fig. 15.3 Isokinetic
sampling