Page 218 - Air and gas Drilling Field Guide 3rd Edition
P. 218
8.4 Water Injection and Formation Water Influx 209
Two chemical reactions can occur when oxygen combines with a hydro-
carbon such as methane CH 4 and ethane C 2 H 6 (and any other hydrocarbons).
The lower order combustion is denoted as deflagration and is in an oxygen-lean
environment. For methane, the deflagration reaction is
CH 4 þ 0:5 O 2 ! CO þ 2 H 2 O ðplus heatÞ:
For ethane, the deflagration process is
C 2 H 6 þ O 2 ! 2 CO þ 3 H 2 O > ðplus heatÞ:
The higher order combustion is denoted as detonation and is in an oxygen-rich
environment. For methane, the detonation reaction is
CH 4 þ 2 O 2 ! CO 2 þ 2 H 2 O ðplus heatÞ:
For ethane, the detonation process is
C 2 H 6 þ 3:5 O 2 ! 2 CO 2 þ 3 H 2 O ðplus heatÞ:
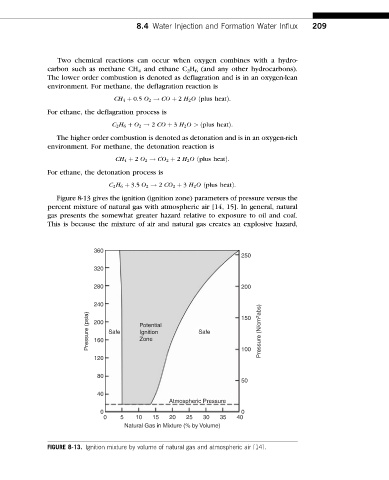
Figure 8-13 gives the ignition (ignition zone) parameters of pressure versus the
percent mixture of natural gas with atmospheric air [14, 15]. In general, natural
gas presents the somewhat greater hazard relative to exposure to oil and coal.
This is because the mixture of air and natural gas creates an explosive hazard,
360
250
320
280 200
240
Pressure (psia) 200 Safe Potential Safe 150 Pressure (N/cm 2 abs)
Ignition
Zone
160
120 100
80
50
40
Atmospheric Pressure
0 0
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
Natural Gas in Mixture (% by Volume)
FIGURE 8-13. Ignition mixture by volume of natural gas and atmospheric air [14].