Page 34 - Air and gas Drilling Field Guide 3rd Edition
P. 34
2.3 Comparison of Mud and Air Drilling 25
P , γ , T e P , γ , T i
e
e
i
i
i − injection
a − above bit
b − below bit
c − collar annulus
p − pipe annulus
P , γ p , T p
p
e − exit
10,000’
(3048m)
500’
P , γ , T c (152m)
c
c
P , γ , T a
a
a
P , γ , T b
b
b
7 /8” (200.1 mm)
7
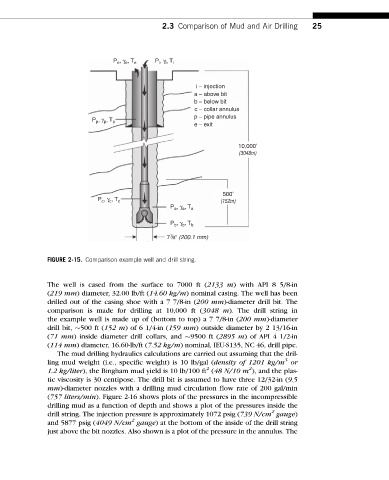
FIGURE 2-15. Comparison example well and drill string.
The well is cased from the surface to 7000 ft (2133 m) with API 8 5/8-in
(219 mm) diameter, 32.00 lb/ft (14.60 kg/m) nominal casing. The well has been
drilled out of the casing shoe with a 7 7/8-in (200 mm)-diameter drill bit. The
comparison is made for drilling at 10,000 ft (3048 m). The drill string in
the example well is made up of (bottom to top) a 7 7/8-in (200 mm)-diameter
drill bit, 500 ft (152 m) of 6 1/4-in (159 mm) outside diameter by 2 13/16-in
(71 mm) inside diameter drill collars, and 9500 ft (2895 m) of API 4 1/2-in
(114 mm) diameter, 16.60-lb/ft (7.52 kg/m) nominal, IEU-S135, NC 46, drill pipe.
The mud drilling hydraulics calculations are carried out assuming that the dril-
3
ling mud weight (i.e., specific weight) is 10 lb/gal (density of 1201 kg/m or
2
2
1.2 kg/liter), the Bingham mud yield is 10 lb/100 ft (48 N/10 m ), and the plas-
tic viscosity is 30 centipose. The drill bit is assumed to have three 12/32-in (9.5
mm)-diameter nozzles with a drilling mud circulation flow rate of 200 gal/min
(757 liters/min). Figure 2-16 shows plots of the pressures in the incompressible
drilling mud as a function of depth and shows a plot of the pressures inside the
2
drill string. The injection pressure is approximately 1072 psig (739 N/cm gauge)
2
and 5877 psig (4049 N/cm gauge) at the bottom of the inside of the drill string
just above the bit nozzles. Also shown is a plot of the pressure in the annulus. The