Page 35 - Air and gas Drilling Field Guide 3rd Edition
P. 35
26 CHAPTER 2 Air and Gas Versus Mud
Pressure (psig)
0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000
0 0
Injection
−500
−2000
Exit Inside Drill String
−1000
−4000
Depth (ft) −1500 Depth (m)
−6000 Annulus
−2000
Bit
−8000
−2500
−10000 −3000
0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 3500 4000
Pressure (N/cm 2 gauge)
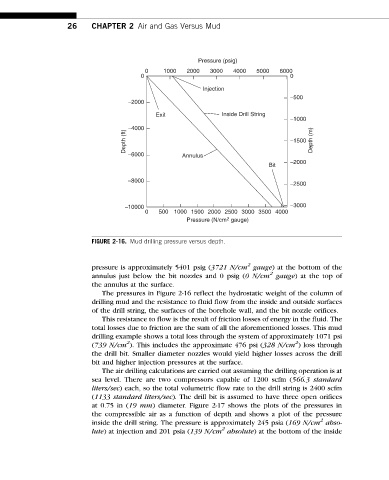
FIGURE 2-16. Mud drilling pressure versus depth.
2
pressure is approximately 5401 psig (3721 N/cm gauge) at the bottom of the
2
annulus just below the bit nozzles and 0 psig (0 N/cm gauge) at the top of
the annulus at the surface.
The pressures in Figure 2-16 reflect the hydrostatic weight of the column of
drilling mud and the resistance to fluid flow from the inside and outside surfaces
of the drill string, the surfaces of the borehole wall, and the bit nozzle orifices.
This resistance to flow is the result of friction losses of energy in the fluid. The
total losses due to friction are the sum of all the aforementioned losses. This mud
drilling example shows a total loss through the system of approximately 1071 psi
2
2
(739 N/cm ). This includes the approximate 476 psi (328 N/cm ) loss through
the drill bit. Smaller diameter nozzles would yield higher losses across the drill
bit and higher injection pressures at the surface.
The air drilling calculations are carried out assuming the drilling operation is at
sea level. There are two compressors capable of 1200 scfm (566.3 standard
liters/sec) each, so the total volumetric flow rate to the drill string is 2400 scfm
(1133 standard liters/sec). The drill bit is assumed to have three open orifices
at 0.75 in (19 mm) diameter. Figure 2-17 shows the plots of the pressures in
the compressible air as a function of depth and shows a plot of the pressure
2
inside the drill string. The pressure is approximately 245 psia (169 N/cm abso-
2
lute) at injection and 201 psia (139 N/cm absolute) at the bottom of the inside