Page 116 - Aircraft Stuctures for Engineering Student
P. 116
100 Energy methods of structural analysis
-ve B.M. (Decreasing Curvature)
0.187 M,
2
moment M,
(a) (b)
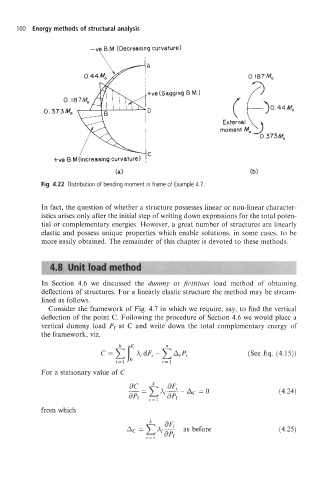
Fig. 4.22 Distribution of bending moment in frame of Example 4.7.
In fact, the question of whether a structure possesses linear or non-linear character-
istics arises only after the initial step of writing down expressions for the total poten-
tial or complementary energies. However, a great number of structures are linearly
elastic and possess unique properties which enable solutions, in some cases, to be
more easily obtained. The remainder of this chapter is devoted to these methods.
In Section 4.6 we discussed the dummy or fictitious load method of obtaining
deflections of structures. For a linearly elastic structure the method may be stream-
lined as follows.
Consider the framework of Fig. 4.7 in which we require, say, to find the vertical
deflection of the point C. Following the procedure of Section 4.6 we would place a
vertical dummy load Pf at C and write down the total complementary energy of
the framework, viz.
k n
Xi dFi - Alpr (See Eq. (4.15))
i= 1 r=l
For a stationary value of C
(4.24)
from which
dFi
A, = c - as before (4.25)
Xi
i= 1 apf