Page 126 - Aircraft Stuctures for Engineering Student
P. 126
1 10 Energy methods of structural analysis
Argyris, J. H. and Kelsey, S., Energy Theorems and Structural Analysis, Butterworths, London,
1960.
Hoff, N. J., The Analysis of Structures, John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York, 1956.
Timoshenko, S. P. and Gere, J. M., Theory of Elastic Stability, McGraw-Hill Book Company,
New York, 1961.
.-. . .
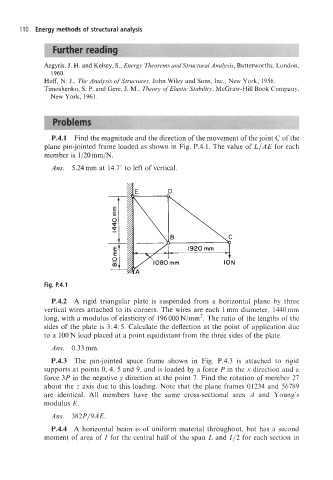
P.4.1 Find the magnitude and the direction of the movement of the joint C of the
plane pin-jointed frame loaded as shown in Fig. P.4.1. The value of LIAE for each
member is 1 /20 mm/N.
Ans. 5.24mm at 14.7" to left of vertical.
Fig. P.4.1
P.4.2 A rigid triangular plate is suspended from a horizontal plane by three
vertical wires attached to its corners. The wires are each 1 mm diameter, 1440mm
long, with a modulus of elasticity of 196 000 N/mm2. The ratio of the lengths of the
sides of the plate is 3:4:5. Calculate the deflection at the point of application due
to a lOON load placed at a point equidistant from the three sides of the plate.
Ans. 0.33mm.
P.4.3 The pin-jointed space frame shown in Fig. P.4.3 is attached to rigid
supports at points 0, 4, 5 and 9, and is loaded by a force P in the x direction and a
force 3P in the negative y direction at the point 7. Find the rotation of member 27
about the z axis due to this loading. Note that the plane frames 01234 and 56789
are identical. All members have the same cross-sectional area A and Young's
modulus E.
Ans. 382P19AE.
P.4.4 A horizontal beam is of uniform material throughout, but has a second
moment of area of 1 for the central half of the span L and 1/2 for each section in