Page 128 - Aircraft Stuctures for Engineering Student
P. 128
1 12 Energy methods of structural analysis
P.4.6 A simply supported beam AB of span L and uniform section carries a
distributed load of intensity varying from zero at A to wo/unit length at B according
to the law
L
w=””(l-&)
per unit length. If the deflected shape of the beam is given approximately by the
expression
n-2
21 = u1 sin- + u2 sin- 2x2
L L
evaluate the coefficients ul and a2 and find the deflection of the beam at mid-span.
Ans. a1 = 2w0L4(7? + 4)/EIr7, a2 = -w0L4/16EI2, O.O0918woL4/EI.
P.4.7 A uniform simply supported beam, span L, carries a distributed loading
which vanes according to a parabolic law across the span. The load intensity is
zero at both ends of the beam and wo at its mid-point. The loading is normal to a
principal axis of the beam cross-section and the relevant flexural rigidity is EI.
Assuming that the deflected shape of the beam can be represented by the series
33 im
Y = ai sin- ‘
i=l
find the coefficients ui and the deflection at the mid-span of the beam using the first
term only in the above series.
Am. ai = 32w0L4/EI7r7i7 (iodd), w0L4/94.4EI.
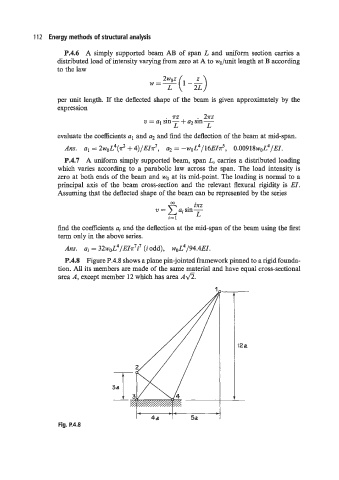
P.4.8 Figure P.4.8 shows a plane pin-jointed framework pinned to a rigid founda-
tion. All its members are made of the same material and have equal cross-sectional
area A, except member 12 which has area A&.
4a 5a
Fig. P.4.8