Page 135 - Aircraft Stuctures for Engineering Student
P. 135
Problems 119
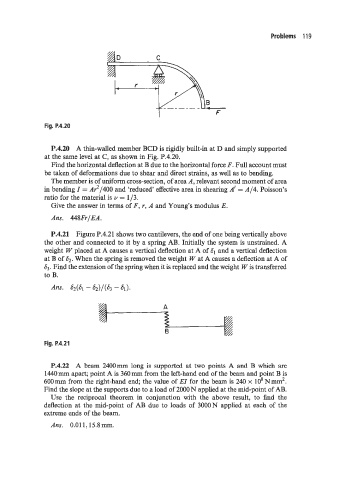
Fig. P.4.20
P.4.20 A thin-walled member BCD is rigidly built-in at D and simply supported
at the same level at C, as shown in Fig. P.4.20.
Find the horizontal deflection at B due to the horizontal force F. Full account must
be taken of deformations due to shear and direct strains, as well as to bending.
The member is of uniform cross-section, of area A, relevant second moment of area
in bending Z = A?/400 and ‘reduced‘ effective area in shearing A‘ = A/4. Poisson’s
ratio for the material is v = 1/3.
Give the answer in terms of F, r, A and Young’s modulus E.
Ans. 448FrlEA.
P.4.21 Figure P.4.21 shows two cantilevers, the end of one being vertically above
the other and connected to it by a spring AB. Initially the system is unstrained. A
weight W placed at A causes a vertical deflection at A of SI and a vertical deflection
at B of 6,. When the spring is removed the weight W at A causes a deflection at A of
6,. Find the extension of the spring when it is replaced and the weight W is transferred
to B.
Ans. &(Si - S,)/(S3 - SI).
Fig. P.4.21
P.4.22 A beam 2400mm long is supported at two points A and B which are
144Omm apart; point A is 360- from the left-hand end of the beam and point B is
600 mm from the right-hand end; the value of EZ for the beam is 240 x lo8 N mm2.
Find the slope at the supports due to a load of 2000N applied at the mid-point of AB.
Use the reciprocal theorem in conjunction with the above result, to find the
deflection at the mid-point of AB due to loads of 3000N applied at each of the
extreme ends of the beam.
Ans. 0.011,15.8mm.