Page 167 - An Introduction to Microelectromechanical Systems Engineering
P. 167
146 MEM Structures and Systems in Photonic Applications
degradation in the performance and tunability of the laser. One such degradation is
mode hopping, when the cavity no longer supports an integral number of half wave-
lengths, causing the laser to “hop” to a different cavity mode (or wavelength) that
satisfies the resonance condition.
Past designs of Littman-Metcalf-type lasers incorporated large traditional
actuators, such as piezoelectric rods or voice-coil actuators, to rotate the mirror
around the virtual pivot point. The Iolon approach uniquely incorporates an
electrostatic rotary microactuator to miniaturize the overall size of the laser (see
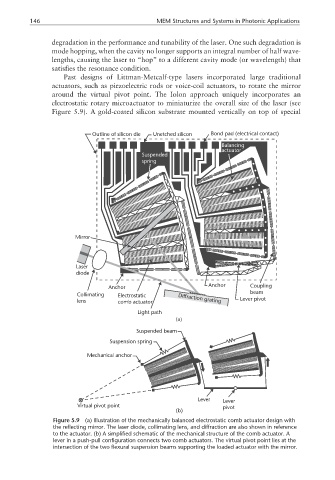
Figure 5.9). A gold-coated silicon substrate mounted vertically on top of special
Outline of silicon die Unetched silicon Bond pad (electrical contact)
Balancing
actuator
Suspended
spring
Mirror
Laser
diode
Anchor Coupling
Anchor
beam
Collimating Electrostatic
lens comb actuator Diffraction grating Lever pivot
Light path
(a)
Suspended beam
Suspension spring
Mechanical anchor
Lever Lever
Virtual pivot point pivot
(b)
Figure 5.9 (a) Illustration of the mechanically balanced electrostatic comb actuator design with
the reflecting mirror. The laser diode, collimating lens, and diffraction are also shown in reference
to the actuator. (b) A simplified schematic of the mechanical structure of the comb actuator. A
lever in a push-pull configuration connects two comb actuators. The virtual pivot point lies at the
intersection of the two flexural suspension beams supporting the loaded actuator with the mirror.