Page 55 - An Introduction to Microelectromechanical Systems Engineering
P. 55
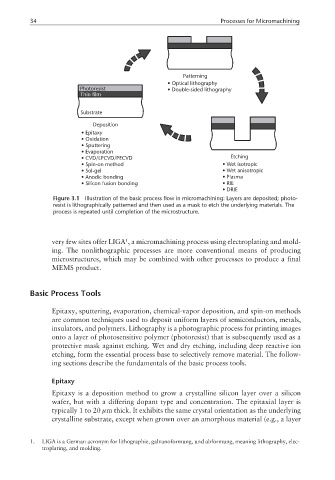
34 Processes for Micromachining
Patterning
• Optical lithography
Photoresist • Double-sided lithography
Thin film
Substrate
Deposition
• Epitaxy
• Oxidation
• Sputtering
• Evaporation
• CVD/LPCVD/PECVD Etching
• Spin-on method • Wet isotropic
• Sol-gel • Wet anisotropic
• Anodic bonding • Plasma
• Silicon fusion bonding • RIE
• DRIE
Figure 3.1 Illustration of the basic process flow in micromachining: Layers are deposited; photo-
resist is lithographically patterned and then used as a mask to etch the underlying materials. The
process is repeated until completion of the microstructure.
very few sites offer LIGA , a micromachining process using electroplating and mold-
1
ing. The nonlithographic processes are more conventional means of producing
microstructures, which may be combined with other processes to produce a final
MEMS product.
Basic Process Tools
Epitaxy, sputtering, evaporation, chemical-vapor deposition, and spin-on methods
are common techniques used to deposit uniform layers of semiconductors, metals,
insulators, and polymers. Lithography is a photographic process for printing images
onto a layer of photosensitive polymer (photoresist) that is subsequently used as a
protective mask against etching. Wet and dry etching, including deep reactive ion
etching, form the essential process base to selectively remove material. The follow-
ing sections describe the fundamentals of the basic process tools.
Epitaxy
Epitaxy is a deposition method to grow a crystalline silicon layer over a silicon
wafer, but with a differing dopant type and concentration. The epitaxial layer is
typically 1 to 20 µm thick. It exhibits the same crystal orientation as the underlying
crystalline substrate, except when grown over an amorphous material (e.g., a layer
1. LIGA is a German acronym for lithographie, galvanoformung, und abformung, meaning lithography, elec-
troplating, and molding.