Page 278 - Analysis and Design of Energy Geostructures
P. 278
Thermohydromechanical behaviour of soils and soil structure interfaces 253
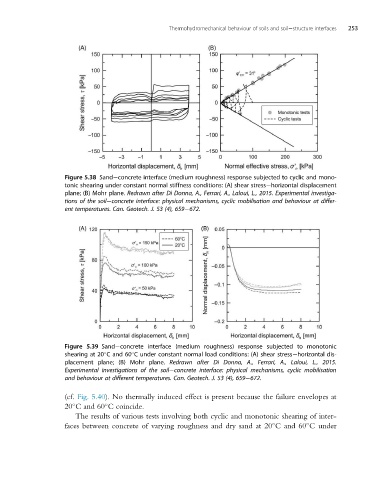
Figure 5.38 Sand concrete interface (medium roughness) response subjected to cyclic and mono-
tonic shearing under constant normal stiffness conditions: (A) shear stress horizontal displacement
plane; (B) Mohr plane. Redrawn after Di Donna, A., Ferrari, A., Laloui, L., 2015. Experimental investiga-
tions of the soil concrete interface: physical mechanisms, cyclic mobilisation and behaviour at differ-
ent temperatures. Can. Geotech. J. 53 (4), 659 672.
Figure 5.39 Sand concrete interface (medium roughness) response subjected to monotonic
shearing at 20 C and 60 C under constant normal load conditions: (A) shear stress horizontal dis-
placement plane; (B) Mohr plane. Redrawn after Di Donna, A., Ferrari, A., Laloui, L., 2015.
Experimental investigations of the soil concrete interface: physical mechanisms, cyclic mobilisation
and behaviour at different temperatures. Can. Geotech. J. 53 (4), 659 672.
(cf. Fig. 5.40). No thermally induced effect is present because the failure envelopes at
20 C and 60 C coincide.
The results of various tests involving both cyclic and monotonic shearing of inter-
faces between concrete of varying roughness and dry sand at 20 C and 60 C under