Page 99 - Analysis and Design of Machine Elements
P. 99
Detachable Joints and Fastening Methods
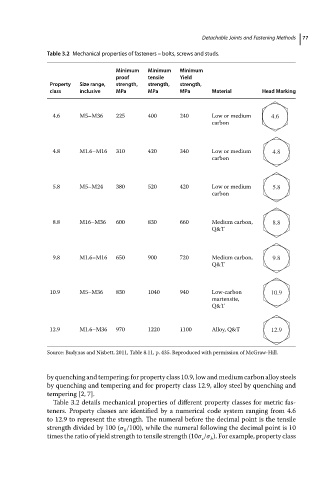
Table 3.2 Mechanical properties of fasteners – bolts, screws and studs. 77
Minimum Minimum Minimum
proof tensile Yield
Property Size range, strength, strength, strength,
class inclusive MPa MPa MPa Material Head Marking
4.6 M5–M36 225 400 240 Low or medium 4.6
carbon
4.8 M1.6–M16 310 420 340 Low or medium 4.8
carbon
5.8 M5–M24 380 520 420 Low or medium 5.8
carbon
8.8 M16–M36 600 830 660 Medium carbon, 8.8
Q&T
9.8 M1.6–M16 650 900 720 Medium carbon, 9.8
Q&T
10.9 M5–M36 830 1040 940 Low-carbon 10.9
martensite,
Q&T
12.9 M1.6–M36 970 1220 1100 Alloy, Q&T 12.9
Source: Budynas and Nisbett, 2011, Table 8.11, p. 435. Reproduced with permission of McGraw-Hill.
by quenching and tempering; for property class 10.9, low and medium carbon alloy steels
by quenching and tempering and for property class 12.9, alloy steel by quenching and
tempering [2, 7].
Table 3.2 details mechanical properties of different property classes for metric fas-
teners. Property classes are identified by a numerical code system ranging from 4.6
to 12.9 to represent the strength. The numeral before the decimal point is the tensile
strength divided by 100 ( /100), while the numeral following the decimal point is 10
b
times the ratio of yield strength to tensile strength (10 / ). For example, property class
b
s