Page 163 - Analytical Electrochemistry 2d Ed - Jospeh Wang
P. 163
148 POTENTIOMETRY
selectivity was reported by Cremer in 1906 (14). Glass pH electrodes of different
con®gurations and dimensions have been in routine use for over six decades since
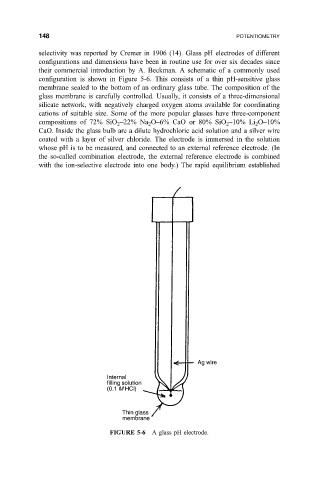
their commercial introduction by A. Beckman. A schematic of a commonly used
con®guration is shown in Figure 5-6. This consists of a thin pH-sensitive glass
membrane sealed to the bottom of an ordinary glass tube. The composition of the
glass membrane is carefully controlled. Usually, it consists of a three-dimensional
silicate network, with negatively charged oxygen atoms available for coordinating
cations of suitable size. Some of the more popular glasses have three-component
compositions of 72% SiO 2 ±22% Na 2 O±6% CaO or 80% SiO 2 ±10% Li 2 O±10%
CaO. Inside the glass bulb are a dilute hydrochloric acid solution and a silver wire
coated with a layer of silver chloride. The electrode is immersed in the solution
whose pH is to be measured, and connected to an external reference electrode. (In
the so-called combination electrode, the external reference electrode is combined
with the ion-selective electrode into one body.) The rapid equilibrium established
FIGURE 5-6 A glass pH electrode.