Page 51 - Anthropometry, Apparel Sizing and Design
P. 51
Anthropometric methods for apparel design: Body measurement devices and techniques 47
Table 2.3 Continued
ISO 8559-1 ISO 7250-1 Comparison
5.3.19 Wrist girth 6.4.12 Wrist Not identical: the tape measure
circumference passes the wrist point in ISO
8559-1, while the tape measure
passes at the level of radial
stylion and just distal to the
ulnar stylion in ISO 7250-1
5.5.2 Hand length (wrist 6.3.1 Hand length Not identical: hand length is
crease) (stylion) measured from the distal wrist
crease in ISO 8559-1, while it is
measured from the line
connecting the radial stylion
and ulnar stylion in ISO 7250-1
5.5.3 Palm length 6.3.2 Palm length Not identical: palm length is
perpendicular measured from the distal wrist
crease in ISO 8559-1, while it is
measured from the line
connecting the radial stylion
and ulnar stylion in ISO 7250-1
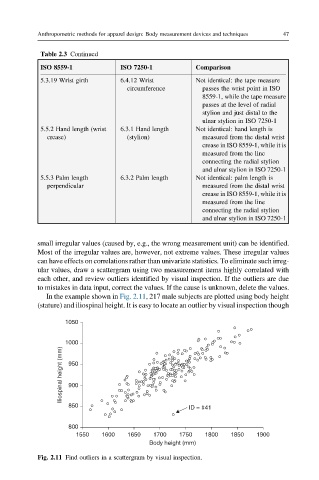
small irregular values (caused by, e.g., the wrong measurement unit) can be identified.
Most of the irregular values are, however, not extreme values. These irregular values
can have effects on correlations rather than univariate statistics. To eliminate such irreg-
ular values, draw a scattergram using two measurement items highly correlated with
each other, and review outliers identified by visual inspection. If the outliers are due
to mistakes in data input, correct the values. If the cause is unknown, delete the values.
In the example shown in Fig. 2.11, 217 male subjects are plotted using body height
(stature) and iliospinal height. It is easy to locate an outlier by visual inspection though
Fig. 2.11 Find outliers in a scattergram by visual inspection.