Page 17 - Applied Process Design For Chemical And Petrochemical Plants Volume III
P. 17
66131_Ludwig_CH10A 5/30/2001 4:06 PM Page 7
Heat Transfer 7
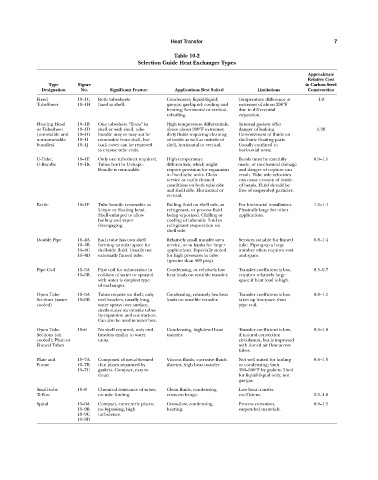
Table 10-2
Selection Guide Heat Exchanger Types
Approximate
Relative Cost
Type Figure in Carbon Steel
Designation No. Significant Feature Applications Best Suited Limitations Construction
Fixed 10—1C Both tubesheets Condensers; liquid-liquid; Temperature difference at 1.0
TubeSheet 10—1H fixed to shell. gas-gas; gas-liquid; cooling and extremes of about 200°F
heating, horizontal or vertical, due to differential
reboiling. expansion.
Floating Head 10—1B One tubesheet “floats” in High temperature differentials, Internal gaskets offer
or Tubesheet 10—1D shell or with shell, tube above about 200°F extremes; danger of leaking. 1.28
(removable and 10—1G bundle may or may not be dirty fluids requiring cleaning Corrosiveness of fluids on
nonremovable 10—1I removable from shell, but of inside as well as outside of shell-side floating parts.
bundles) 10—1J back cover can be removed shell, horizontal or vertical. Usually confined to
to expose tube ends. horizontal units.
U-Tube; 10—1E Only one tubesheet required. High temperature Bends must be carefully 0.9—1.1
U-Bundle 10—1K Tubes bent in U-shape. differentials, which might made, or mechanical damage
Bundle is removable. require provision for expansion and danger of rupture can
in fixed tube units. Clean result. Tube side velocities
service or easily cleaned can cause erosion of inside
conditions on both tube side of bends. Fluid should be
and shell side. Horizontal or free of suspended particles.
vertical.
Kettle 10—1F Tube bundle removable as Boiling fluid on shell side, as For horizontal installation. 1.2—1.4
U-type or floating head. refrigerant, or process fluid Physically large for other
Shell enlarged to allow being vaporized. Chilling or applications.
boiling and vapor cooling of tube-side fluid in
disengaging. refrigerant evaporation on
shell side.
Double Pipe 10—4A Each tube has own shell Relatively small transfer area Services suitable for finned 0.8—1.4
10—4B forming annular space for service, or in banks for larger tube. Piping-up a large
10—4C shell-side fluid. Usually use applications. Especially suited number often requires cost
10—4D externally finned tube. for high pressures in tube and space.
(greater than 400 psig).
Pipe Coil 10—5A Pipe coil for submersion in Condensing, or relatively low Transfer coefficient is low, 0.5—0.7
10—5B coil-box of water or sprayed heat loads on sensible transfer. requires relatively large
with water is simplest type space if heat load is high.
of exchanger.
Open Tube 10—5A Tubes require no shell, only Condensing, relatively low heat Transfer coefficient is low, 0.8—1.1
Sections (water 10—5B end headers, usually long, loads on sensible transfer. takes up less space than
cooled) water sprays over surface, pipe coil.
sheds scales on outside tubes
by expansion and contraction.
Can also be used in water box.
Open Tube 10—6 No shell required, only end Condensing, high-level heat Transfer coefficient is low, 0.8—1.8
Sections (air headers similar to water transfer. if natural convection
cooled); Plain or units. circulation, but is improved
Finned Tubes with forced air flow across
tubes.
Plate and 10—7A Composed of metal-formed Viscous fluids, corrosive fluids Not well suited for boiling 0.8—1.5
Frame 10—7B thin plates separated by slurries, high heat transfer. or condensing; limit
10—7C gaskets. Compact, easy to 350—500°F by gaskets. Used
clean. for liquid-liquid only; not
gas-gas.
Small-tube 10—8 Chemical resistance of tubes; Clean fluids, condensing, Low heat transfer
Teflon no tube fouling. cross-exchange. coefficient. 2.0—4.0
Spiral 10—9A Compact, concentric plates; Cross-flow, condensing, Process corrosion, 0.8—1.5
10—9B no bypassing, high heating. suspended materials.
10—9C turbulence.
10—9D