Page 18 - Applied Process Design For Chemical And Petrochemical Plants Volume III
P. 18
66131_Ludwig_CH10A 5/30/2001 4:06 PM Page 8
8 Applied Process Design for Chemical and Petrochemical Plants
Details of Exchange Equipment and many states and insurance companies require compli-
Assembly and Arrangement ance with this.
These classes are explained in the TEMA Standards and
The process design of heat exchange equipment in Rubin. 99, 100, 133
depends to a certain extent upon the basic type of unit con-
sidered for the process and how it will be arranged together
2. Thermal Rating Standards
with certain details of assembly as they pertain to that par-
ticular unit. It is important to recognize that certain basic
The TEMA Code 107 does not recommend thermal
types of exchangers, as given in Table 10-2, are less expen-
design or rating of heat exchangers. This is left to the rat-
sive than others and also that inherently these problems are
ing or design engineer, because many unique details are
related to the fabrication of construction materials to resist
associated with individual applications. TEMA does offer
the fluids, cleaning, future reassignment to other services,
some common practice rating charts and tables, along
etc. The following presentation alerts the designer to the
with some tabulations of selected petroleum and chemical
various features that should be considered. Also see physical property data in the third (1952) and sixth (1978)
Rubin. 281
editions.
1. Construction Codes
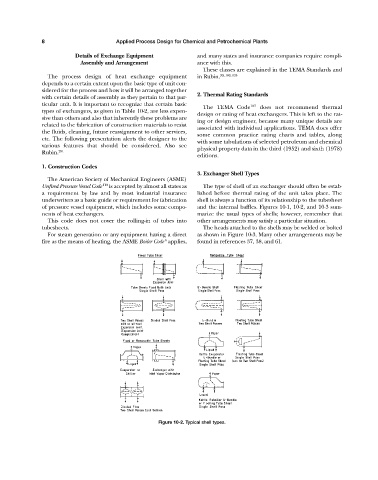
3. Exchanger Shell Types
The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME)
Unfired Pressure Vessel Code 119 is accepted by almost all states as The type of shell of an exchanger should often be estab-
a requirement by law and by most industrial insurance lished before thermal rating of the unit takes place. The
underwriters as a basic guide or requirement for fabrication shell is always a function of its relationship to the tubesheet
of pressure vessel equipment, which includes some compo- and the internal baffles. Figures 10-1, 10-2, and 10-3 sum-
nents of heat exchangers. marize the usual types of shells; however, remember that
This code does not cover the rolling-in of tubes into other arrangements may satisfy a particular situation.
tubesheets. The heads attached to the shells may be welded or bolted
For steam generation or any equipment having a direct as shown in Figure 10-3. Many other arrangements may be
6
fire as the means of heating, the ASME Boiler Code applies, found in references 37, 38, and 61.
Figure 10-2. Typical shell types.