Page 185 - Applied Process Design For Chemical And Petrochemical Plants Volume III
P. 185
66131_Ludwig_CH10E 5/30/2001 4:33 PM Page 148
148 Applied Process Design for Chemical and Petrochemical Plants
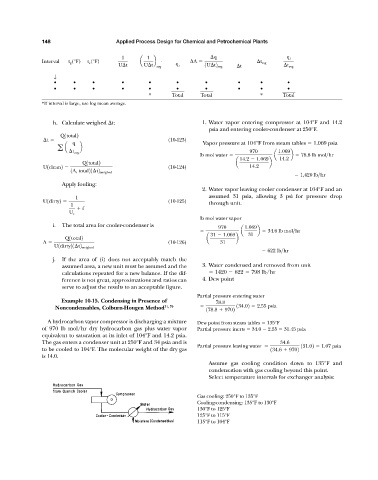
1 1 q q i
Interval t g (°F) t c (°F) a b A t avg
U t U t avg q i 1U t2 avg t t avg
↓
• • • • • • • • • •
• • • • • • • • • •
* Total Total * Total
*If interval is large, use log mean average.
h. Calculate weighed t: 1. Water vapor entering compressor at 104°F and 14.2
psia and entering cooler-condenser at 250°F.
Q1total2
t (10-123)
q Vapor pressure at 104°F from steam tables 1.069 psia
a a b
t avg 970 1.069
lb mol water a b 78.8 lb mol>hr
14.2 1.069 14.2
Q1total2 a b
U1clean2 (10-124) 14.2
1A, total21 t2 weighed
1,420 lb>hr
Apply fouling:
2. Water vapor leaving cooler condenser at 104°F and an
1 assumed 31 psia, allowing 3 psi for pressure drop
U1dirty2 (10-125)
1 through unit.
f
U c
lb mol water vapor
i. The total area for cooler-condenser is 970 1.069
a b 34.6 lb mol>hr
31 1.069 31
Q1total2 a b
A (10-126) 31
U1dirty21 t2 weighed
622 lb>hr
j. If the area of (i) does not acceptably match the
assumed area, a new unit must be assumed and the 3. Water condensed and removed from unit
calculations repeated for a new balance. If the dif- 1420 622 798 lb/hr
ference is not great, approximations and ratios can 4. Dew point
serve to adjust the results to an acceptable figure.
Partial pressure entering water
Example 10-15. Condensing in Presence of 78.8
Noncondensables, Colburn-Hougen Method 31, 70 134.02 2.55 psia
178.8 9702
A hydrocarbon vapor compressor is discharging a mixture Dew point from steam tables 135°F
of 970 lb mol/hr dry hydrocarbon gas plus water vapor Partial pressure inerts 34.0 2.55 31.45 psia
equivalent to saturation at its inlet of 104°F and 14.2 psia.
The gas enters a condenser unit at 250°F and 34 psia and is 34.6
Partial pressure leaving water 131.02 1.07 psia
to be cooled to 104°F. The molecular weight of the dry gas 134.6 9702
is 14.0.
Assume gas cooling condition down to 135°F and
condensation with gas cooling beyond this point.
Select temperature intervals for exchanger analysis:
Gas cooling: 250°F to 135°F
Cooling-condensing: 135°F to 130°F
130°F to 125°F
125°F to 115°F
115°F to 104°F