Page 238 -
P. 238
200 Part III Underbalanced Drilling Systems
Fracture Pressure, p frac
Shutoff Pump
ISIP∼σ h
Pressure σ h
ISIP
Borehole
Volume Time
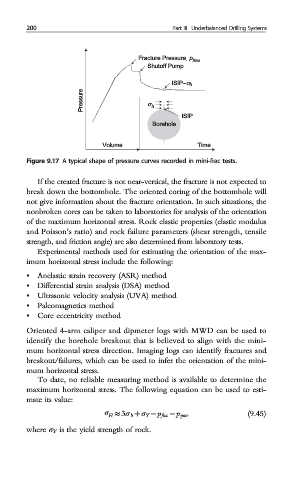
Figure 9.17 A typical shape of pressure curves recorded in mini-frac tests.
If the created fracture is not near-vertical, the fracture is not expected to
break down the bottomhole. The oriented coring of the bottomhole will
not give information about the fracture orientation. In such situations, the
nonbroken cores can be taken to laboratories for analysis of the orientation
of the maximum horizontal stress. Rock elastic properties (elastic modulus
and Poisson’s ratio) and rock failure parameters (shear strength, tensile
strength, and friction angle) are also determined from laboratory tests.
Experimental methods used for estimating the orientation of the max-
imum horizontal stress include the following:
• Anelastic strain recovery (ASR) method
• Differential strain analysis (DSA) method
• Ultrasonic velocity analysis (UVA) method
• Paleomagnetics method
• Core eccentricity method
Oriented 4-arm caliper and dipmeter logs with MWD can be used to
identify the borehole breakout that is believed to align with the mini-
mum horizontal stress direction. Imaging logs can identify fractures and
breakout/failures, which can be used to infer the orientation of the mini-
mum horizontal stress.
To date, no reliable measuring method is available to determine the
maximum horizontal stress. The following equation can be used to esti-
mate its value:
(9.45)
σ H ≈ 3σ h + σ Y − p frac − p pore
where σ Y is the yield strength of rock.