Page 241 -
P. 241
Gas and Liquid Injection Rates 203
Illustrative Example 9.4
A well is to be drilled through a pay zone at a true vertical depth of 4,505 ft
with a pore pressure of 1,802 psia. Additional data are given as follows.
Aeratedliquidisto beusedtoachieve an underbalanced pressure differ-
ential of 300 psi, or borehole pressure 1,502 psia. If the wellbore is drilled
in the direction of the minimum horizontal stress, what is the maximum
allowable inclination angle in the pay zone in order to avoid borehole
collapse?
In situ stresses
Vertical in situ stress, σ V : 4,908 psi
Maximum horizontal stress, σ H : 2,850 psi
Minimum horizontal stress, σ h : 2,650 psi
Rock properties
Cohesive strength, S o : 1,402 psi
Friction angle, ϕ: 39 Deg.
Poisson’s ratio, ν: 0.28
Poroelastic constant, a p : 0.72
Solution
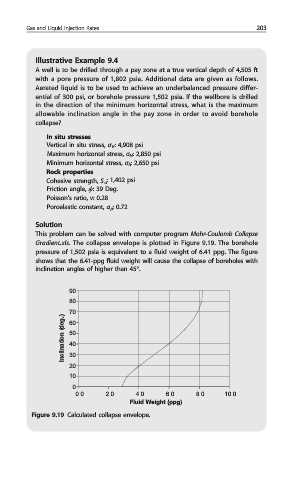
This problem can be solved with computer program Mohr-Coulomb Collapse
Gradient.xls. The collapse envelope is plotted in Figure 9.19. The borehole
pressure of 1,502 psia is equivalent to a fluid weight of 6.41 ppg. The figure
shows that the 6.41-ppg fluid weight will cause the collapse of boreholes with
inclination angles of higher than 45°.
90
80
70
Inclination (deg.) 50
60
40
30
20
10
0
0.0 2.0 4.0 6.0 8.0 10.0
Fluid Weight (ppg)
Figure 9.19 Calculated collapse envelope.