Page 100 - Applied Photovoltaics
P. 100
NOCT 20
T T u S (q C) (5.2)
cell air
800
2
where S is the insolation in W/m . Module temperature will be lower than this when
wind velocity is high, but higher under still conditions. Temperature effects can be
particularly important for building-integrated modules, with care needed to ensure as
much airflow as possible behind the modules to prevent temperature build-up.
Cell packing density also has a bearing on operating temperature, with sparsely
packed cells having a lower NOCT. For example:
x 50% cell packing ĺ 41°C NOCT
x 100% cell packing ĺ 48°C NOCT.
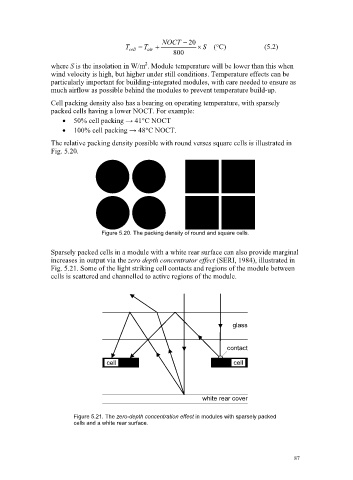
The relative packing density possible with round verses square cells is illustrated in
Fig. 5.20.
Figure 5.20. The packing density of round and square cells.
Sparsely packed cells in a module with a white rear surface can also provide marginal
increases in output via the zero depth concentrator effect (SERI, 1984), illustrated in
Fig. 5.21. Some of the light striking cell contacts and regions of the module between
cells is scattered and channelled to active regions of the module.
glass
contact
cell cell
white rear cover
Figure 5.21. The zero-depth concentration effect in modules with sparsely packed
cells and a white rear surface.
87