Page 301 - APPLIED PROCESS DESIGN FOR CHEMICAL AND PETROCHEMICAL PLANTS, Volume 1, 3rd Edition
P. 301
Mechanical Separations 273
r,orn Dust c. Chemical composition of vapor and of dust,
Sources including any abrasive, hydroscopic or other char-
acteristics.
2. Define dust recovery, as percentage below a certain
particle size.
3. Indicate, if known, preferred bag material that
will withstand environment, e.g., fibers of glass,
polyester, Teflon@, Nomex@, polypropylene, poly-
ethylene, cotton, wool, nylon, Qrlon@, Dacron@,
and Dynel@. The type of weave of fiber should be
recommended by the manufacturer. The fabrics
may be felted or woven [4$,48] in weaves of
plain, satin, or twill, and should be resistant to
to Fan
to Fan
k any corrosive material in the solid particles or
Cleaning Air from the gas stream.
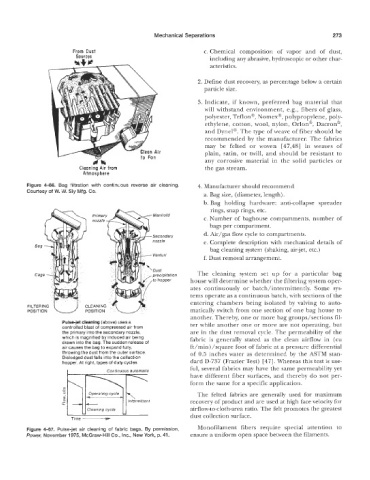
~ ~ ~ a s ~ h ~ g ~
th continuous reverse air cleaning. 4. Manufacturer should recommend
a. Bag size, (diameter, length).
b. Bag holding hardware: anti-collapse spreader
rings, snap rings, etc.
Manjrold
c. Number of baghouse compartments, number of
bags per compartment.
d. Air/gas flow cycle to compartments.
Secondary
nozzle e. Complete description with mechanical details of
bag cleaning system (shaking, air-jet, etc.)
Venturi
f. Dust removal arrangement.
Dust The cleaning system set up for a particular bag
precipitation
to hopper house will determine whether the filtering system oper-
ates continuously or batch/intermittently. Some sys-
tems operate as a continuous batch, with sections of the
entering chambers being isolated by vahing to auto-
FIL TERING
POSITION L/ POSITION matically switch from one section of one bag house to
another. Thereby, one or more bag groups/sections fil-
ulse-jet cleaning (above) uses a ter while another one or more are not operating, but
controlled blast of compressed air from
the primary into the secondary nozzle, are in the dust removal cycle. The permeability of the
which IS magnified by induced air being fabric is generally stated as the clean airflow in (cu
arawn into the bag The sudden release of
air causes the bag to expand fully ft/min) /square foot of fabric at a pressure differential
throwing the dust from the outer surface of 0.5 inches water as determined by the ASTM stan-
Dislodged dust falls into the collection
hopper Pit right, types of duty cycles dard D-737 (Frazier Test) [47]. Whereas this test is use-
ful, several fabrics may have the same permeability yet
I Continuous automafic
have different fiber surfaces, and thereby do not per-
form the same for a specific application.
The felted fabrics are generally used for maximum
recovery of product and are used at high face velocity for
airflow-to-cloth-area ratio. The felt promotes the greatest
dust collection surface.
Time
cleaning of fabric bags. By permission, Monofilament fibers require special attention to
cGraw-Hill Go., Inc., New York, p. 41. ensure a uniform open space between the filaments.