Page 334 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 334
THE NOBLE GASES
314
Interestingly, no added fluoride was needed for a similar reaction between C F XeF and
6 5
C F SiF :
6 5
3
C F XeF + C F SiF → Xe(C F ) + SiF (8.54)
6 5 6 5 3 6 5 2 4
The compound C F XeF has proved to be a versatile starting material for other
6 5
organoxenon compounds, for example, C F XeCN:
6 5
C F XeF + Me SiCN → C F XeCN + Me SiF (8.55)
6 5 3 6 5 3
REVIEW PROBLEM 8.7
Suggest mechanisms for the above silicon-mediated transformations, that is, reactions
8.51 through 8.54.
REVIEW PROBLEM 8.8
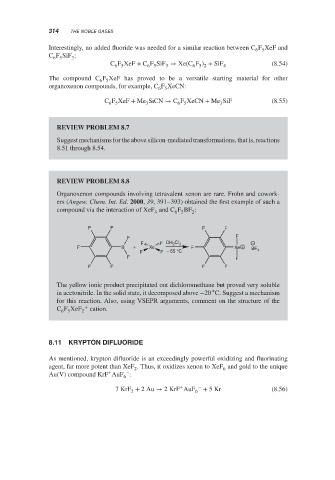
Organoxenon compounds involving tetravalent xenon are rare. Frohn and cowork-
ers (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 391–393) obtained the first example of such a
compound via the interaction of XeF and C F BF :
2
6 5
4
F F F F
F F
F F CH 2 CI 2 −
F B + Xe F Xe + BF
F F − 55 °C 4
F F
F F F F
The yellow ionic product precipitated out dichloromethane but proved very soluble
∘
in acetonitrile. In the solid state, it decomposed above −20 C. Suggest a mechanism
for this reaction. Also, using VSEPR arguments, comment on the structure of the
C F XeF + cation.
6 5 2
8.11 KRYPTON DIFLUORIDE
As mentioned, krypton difluoride is an exceedingly powerful oxidizing and fluorinating
agent, far more potent than XeF . Thus, it oxidizes xenon to XeF and gold to the unique
6
2
+ −
Au(V) compound KrF AuF :
6
+ −
7KrF + 2Au → 2KrF AuF 6 + 5 Kr (8.56)
2