Page 56 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 56
A COLLECTION OF BASIC CONCEPTS
36
Let us work our way through a radical chain reaction. A good example is the photo-
chemical chlorination of alkanes, shown below for methane:
Cl 2 , hν Cl 2
CH 3 Cl
CH 4 CH 2 Cl 2
− HCl − HCl
(1.75)
Cl 2 Cl 2
CHCl 3 CCl 4
− HCl − HCl
The reaction begins with the light-induced splitting of molecular chlorine into chlorine
atoms; this is called the initiation step:
hν
Cl Cl Cl + Cl (1.76)
A chlorine atom can then abstract a hydrogen from methane:
H Cl H
+
C H C H Cl (1.77)
H H
H
H
The methyl radical then abstracts a chlorine atom from molecular chlorine, forming
chloromethane and another chlorine atom, thus perpetuating the presence of chlorine
radicals in the system.
H Cl Cl H
C C Cl + Cl (1.78)
H H
H
H
The above two steps are collectively referred to as propagation steps. A methyl radical and
a chlorine atom may also combine to form chloromethane, as shown below, in what is called
a termination step:
H Cl
H
C C Cl (1.79)
H H
H
H
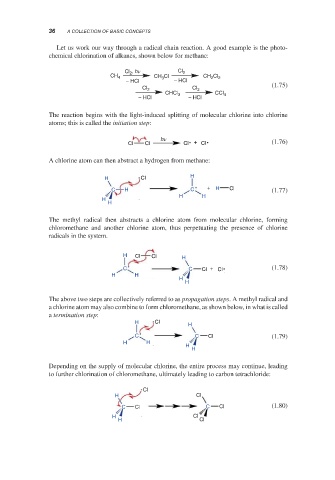
Depending on the supply of molecular chlorine, the entire process may continue, leading
to further chlorination of chloromethane, ultimately leading to carbon tetrachloride:
Cl
H Cl
C Cl C Cl (1.80)
H Cl
H Cl