Page 118 - 05. Subyek Teknik Mesin - Automobile Mechanical and Electrical Systems Automotive Technology Vehicle Maintenance and Repair (Vehicle Maintenance Repr Nv2) by Tom Denton
P. 118
2
102 Automobile mechanical and electrical systems
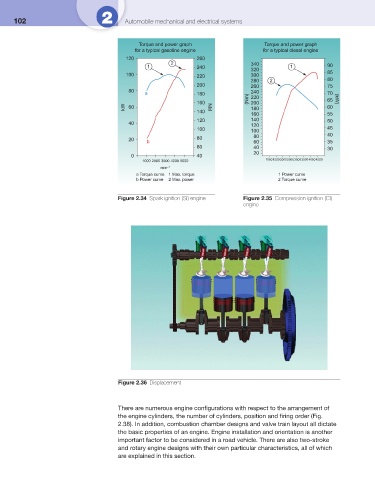
Torque and power graph Torque and power graph
for a typical gasoline engine for a typical diesel engine
120 260
2 340
1 240 1 90
320
100 220 300 85
280 2 80
200 260 75
80 240
a 180 220
160 (Nm) 200 65
kW 60 NM 180 60
70 (kW)
140
160 55
120 140 50
40 120
100 100 45
20 80 80 40
b 60 35
60 40 30
20
0 40
1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 10001500200025003000350040004500
min –1
a Torque curve 1 Max. torque 1 Power curve
b Power curve 2 Max. power 2 Torque curve
Figure 2.34 Spark ignition (SI) engine Figure 2.35 Compression ignition (CI)
engine
Figure 2.36 Displacement
There are numerous engine confi gurations with respect to the arrangement of
the engine cylinders, the number of cylinders, position and fi ring order ( Fig.
2.38 ). In addition, combustion chamber designs and valve train layout all dictate
the basic properties of an engine. Engine installation and orientation is another
important factor to be considered in a road vehicle. There are also two-stroke
and rotary engine designs with their own particular characteristics, all of which
are explained in this section.