Page 120 - 05. Subyek Teknik Mesin - Automobile Mechanical and Electrical Systems Automotive Technology Vehicle Maintenance and Repair (Vehicle Maintenance Repr Nv2) by Tom Denton
P. 120
2
104 Automobile mechanical and electrical systems
Figure 2.39 A single- (left) and four-cylinder (right) engine
1 3
2
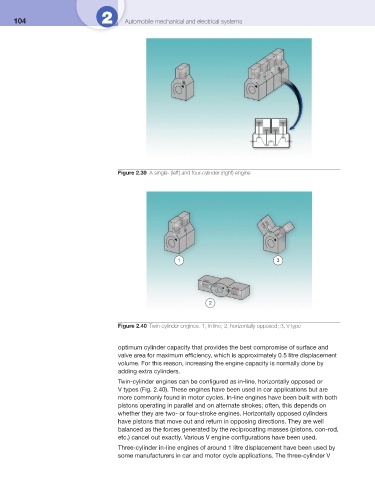
Figure 2.40 Twin-cylinder engines. 1, In-line; 2, horizontally opposed; 3, V type
optimum cylinder capacity that provides the best compromise of surface and
valve area for maximum effi ciency, which is approximately 0.5 litre displacement
volume. For this reason, increasing the engine capacity is normally done by
adding extra cylinders.
Twin-cylinder engines can be confi gured as in-line, horizontally opposed or
V types ( Fig. 2.40 ). These engines have been used in car applications but are
more commonly found in motor cycles. In-line engines have been built with both
pistons operating in parallel and on alternate strokes; often, this depends on
whether they are two- or four-stroke engines. Horizontally opposed cylinders
have pistons that move out and return in opposing directions. They are well
balanced as the forces generated by the reciprocating masses (pistons, con-rod,
etc.) cancel out exactly. Various V engine confi gurations have been used.
Three-cylinder in-line engines of around 1 litre displacement have been used by
some manufacturers in car and motor cycle applications. The three-cylinder V